Stainless Steel 3D Printing Technology: Everything You Have to Know
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by additive manufacturing (AM). Among its most impactful applications is the 3D printing of stainless steel, a technology that bridges the gap between design freedom and the robust, corrosion-resistant properties of one of industry's most trusted material families. Moving beyond prototyping, stainless steel AM is now a viable production method for complex, high-performance end-use parts across aerospace, chemical processing, and medical sectors. This guide explores the core principles, processes, materials, and benefits of this revolutionary technology.
Understanding the Core Technology: Metal Powder Bed Fusion
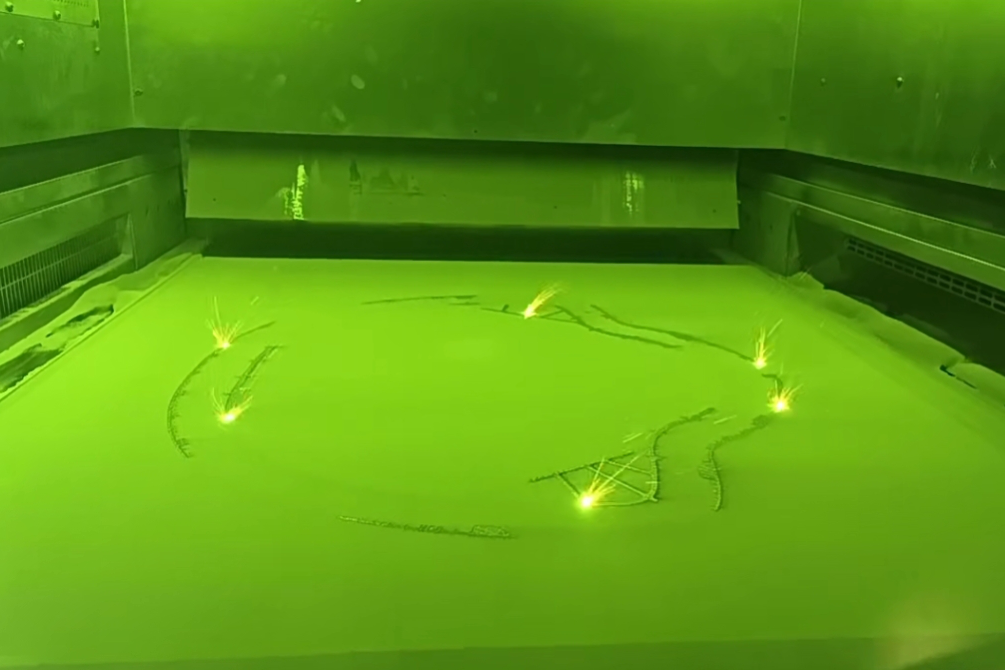
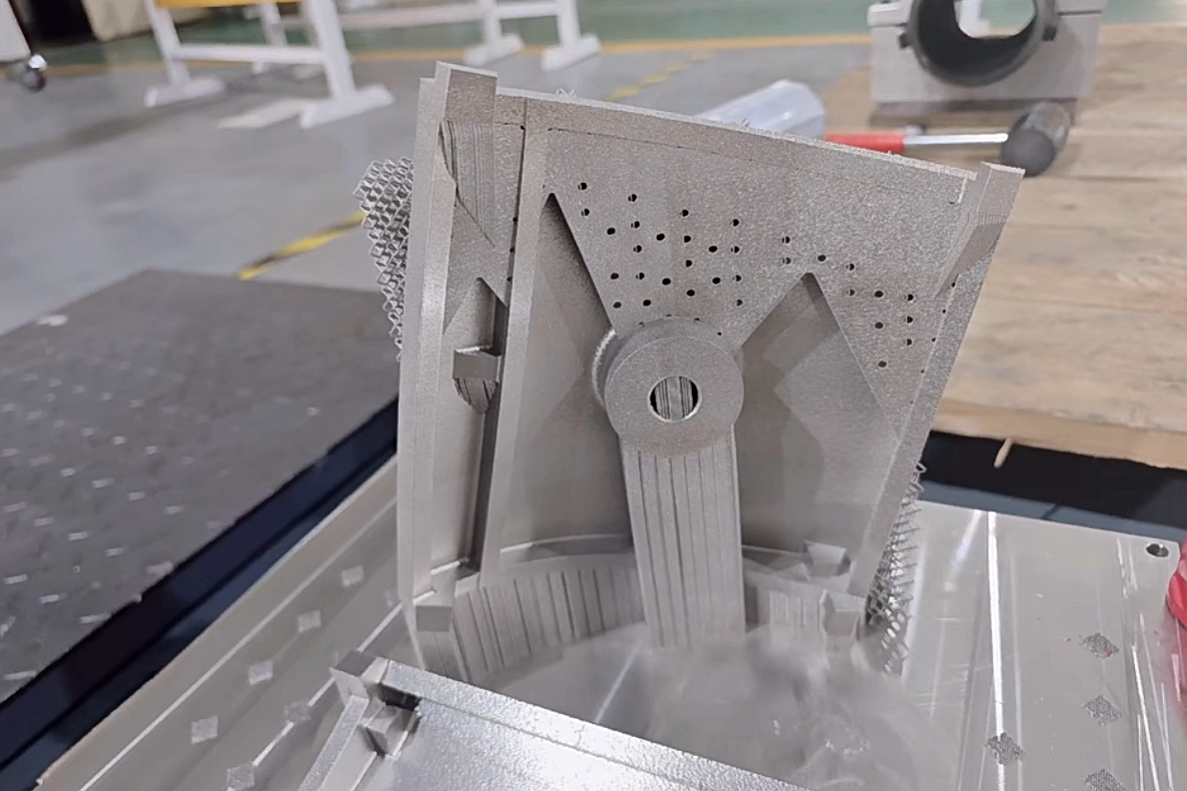
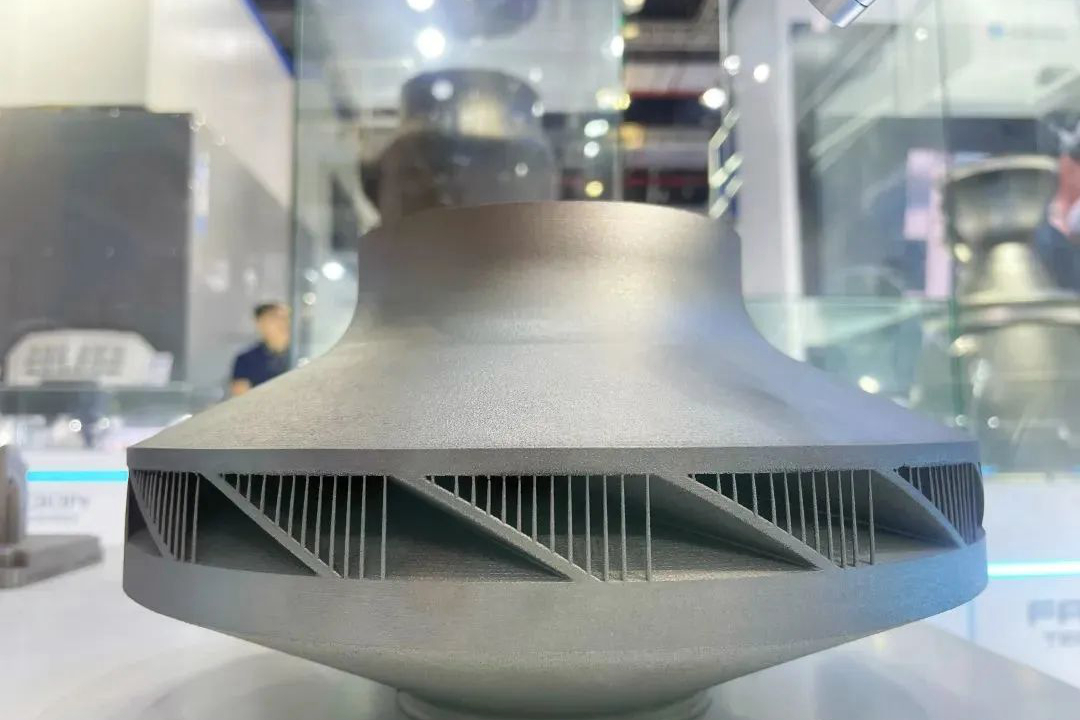
Stainless steel 3D printing for industrial applications predominantly utilizes a process called Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) or Selective Laser Melting (SLM). In this process, a high-power laser selectively scans and melts ultra-fine layers of stainless steel powder, fusing them together based on a 3D CAD model. This occurs layer-by-layer in a sealed chamber filled with inert gas (typically argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. The precision of the laser and the thinness of each layer (typically 20-60 microns) allow for the creation of geometries that are impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional casting or machining, including internal channels, lattice structures, and topology-optimized lightweight forms.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Manufacturing
Adopting stainless steel 3D printing offers a compelling set of benefits that solve long-standing engineering challenges: Unparalleled Design Freedom: Create consolidated assemblies, integrated cooling channels, and organic shapes that minimize weight while maximizing function. Rapid Prototyping to Production: Accelerate development cycles by iterating functional metal prototypes quickly and transition seamlessly to small-batch or on-demand production. Material Efficiency & Waste Reduction: The additive nature of the process uses only the material needed for the part and support structures, contrasting sharply with the subtractive waste of CNC machining. Performance-Optimized Parts: The rapid solidification from the melt pool results in a fine, homogeneous microstructure, often yielding mechanical properties that meet or exceed those of wrought or cast equivalents.
The Stainless Steel 3D Printing Workflow: From File to Finished Part
Producing a qualified 3D-printed stainless steel component involves a meticulous, multi-stage process: 1. Design & File Preparation (Digital): The process begins with a 3D model optimized for AM (considering overhangs, support placement, and residual stress). The model is "sliced" into digital layers. 2. Powder Preparation & Machine Setup: High-quality, gas-atomized stainless steel powder (e.g., 316L) is loaded into the printer. The build platform is leveled, and the chamber is purged with inert gas. 3. The Printing Process: The laser meticulously fuses each cross-section. After each layer, the powder bed lowers, a new layer of powder is recoated, and the process repeats until the part is complete. 4. Post-Processing: This is critical for achieving final properties. Steps include:
Support Removal: Printed parts are removed from the build plate, and support structures are detached.
Stress Relief & Heat Treatment: Parts undergo targeted heat treatment to relieve internal stresses and optimize microstructure and mechanical properties.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): For critical applications, HIP is used to eliminate internal micro-porosity, enhancing fatigue life and ductility.
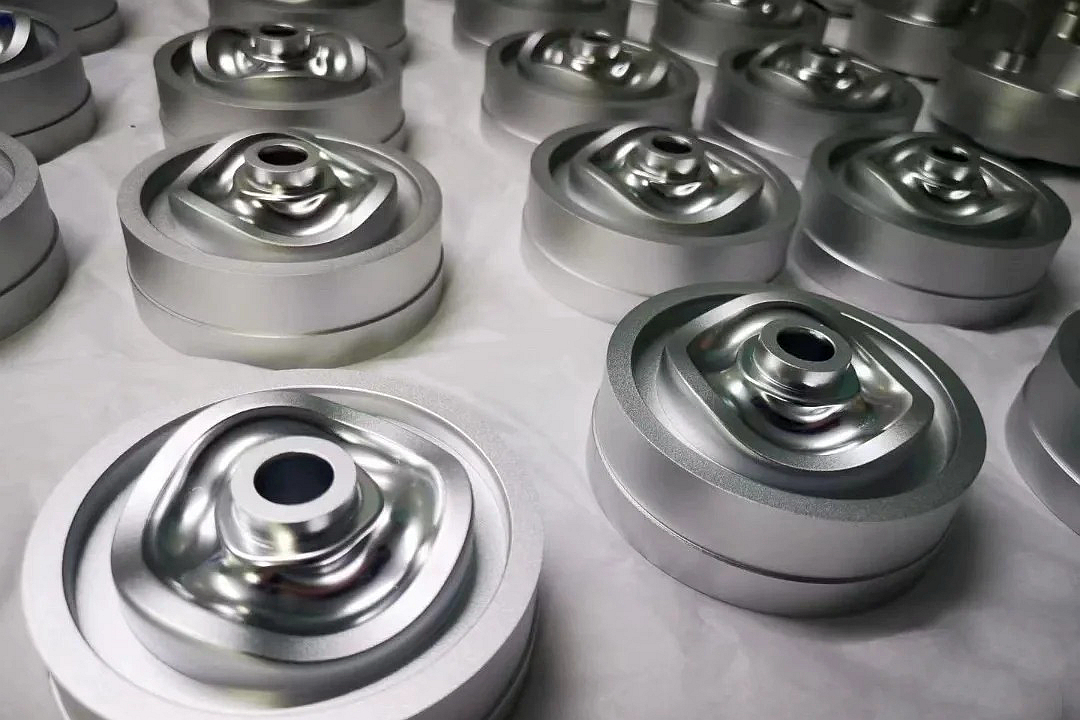
Surface Finish & Machining: Various techniques, from abrasive blasting to precision CNC machining on critical interfaces, achieve the required surface quality and dimensional tolerances.
Key Stainless Steel Materials for AM and Their Properties
The choice of material dictates the part's performance. Neway offers expertise in printing the most widely used and demanding stainless steel alloys: 316L Stainless Steel: The workhorse of corrosion-resistant AM. It offers excellent general corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for marine, chemical, and certain medical applications. 17-4 PH (Precipitation-Hardening) Stainless Steel: This martensitic grade can be age-hardened after printing to achieve very high strength and hardness while maintaining good corrosion resistance. It is perfect for structural components, gears, and tooling. Explore our capabilities with 17-4 PH. 15-5 PH Stainless Steel: Similar to 17-4PH but with improved toughness and transverse mechanical properties. It is favored for high-integrity aerospace and defense components. Learn more about 15-5PH. Specialty Tool Steels & Maraging Steels: For applications requiring extreme wear resistance, hardness, and strength after aging, such as molds, dies, and high-stress industrial parts.
Transforming Industries: Primary Applications
Stainless steel 3D printing is enabling innovation across a spectrum of high-value industries: Aerospace & Defense: Manufacturing lightweight, consolidated brackets, fluid system components, and engine parts with complex internal cooling. The technology supports both defense and commercial aviation needs. Medical & Dental: Producing patient-specific surgical guides, implants (where allowed by regulation), and custom surgical instruments from biocompatible 316L or Ti-6Al-4V (though titanium is a different material family). Energy & Chemical Processing: Creating corrosion-resistant valves, pump impellers, and heat exchanger components with optimized internal passages for the chemical and oil & gas sectors. Industrial Tooling & Automotive: Developing conformal-cooled injection molds for faster cycle times and manufacturing lightweight, high-strength components for automotive and heavy machinery.
Neway's Holistic Approach to Stainless Steel Additive Manufacturing
At Neway, we view 3D printing not as a standalone service but as an integrated node within our advanced manufacturing ecosystem. Our 3D printing services are backed by decades of metallurgical expertise. We provide: End-to-End Solution: From design for AM (DfAM) consulting and material selection to printing, comprehensive post-processing, and quality validation. Material & Process Expertise: Our deep knowledge in powder metallurgy and heat treatment ensures optimal parameters for each stainless steel grade. Rigorous Quality Assurance: Every part is subject to stringent material testing and analysis, including dimensional inspection, density measurement, and mechanical testing, ensuring compliance with the most demanding specifications.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Metal Part Production
Stainless steel 3D printing has matured from a novel prototyping tool into a core industrial manufacturing technology. It empowers engineers to break free from traditional design constraints, optimize part performance, and streamline supply chains for complex, low-volume components. As the technology continues to evolve in speed, material variety, and cost-effectiveness, its adoption will only broaden. By partnering with an experienced manufacturer like Neway, who offers deep metallurgical knowledge and full-process control, you can confidently leverage this transformative technology to build a more innovative and efficient future.
FAQs
How do the mechanical properties of 3D-printed 316L compare to wrought 316L?
What are the typical Ra of as-printed stainless steel parts, and what finishing options exist?
What is the maximum build size for stainless steel components in your 3D printing systems?
What certifications and testing reports are provided for critical stainless steel 3D-printed parts?