Corrax (CX)
Material Introduction
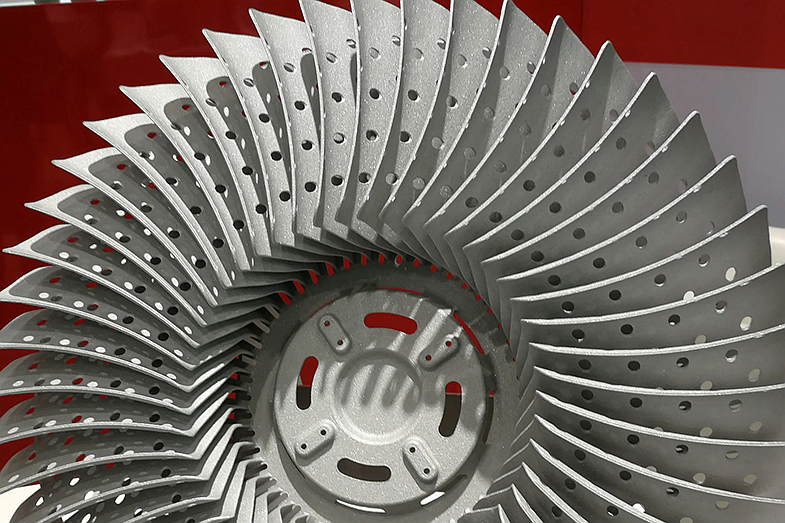
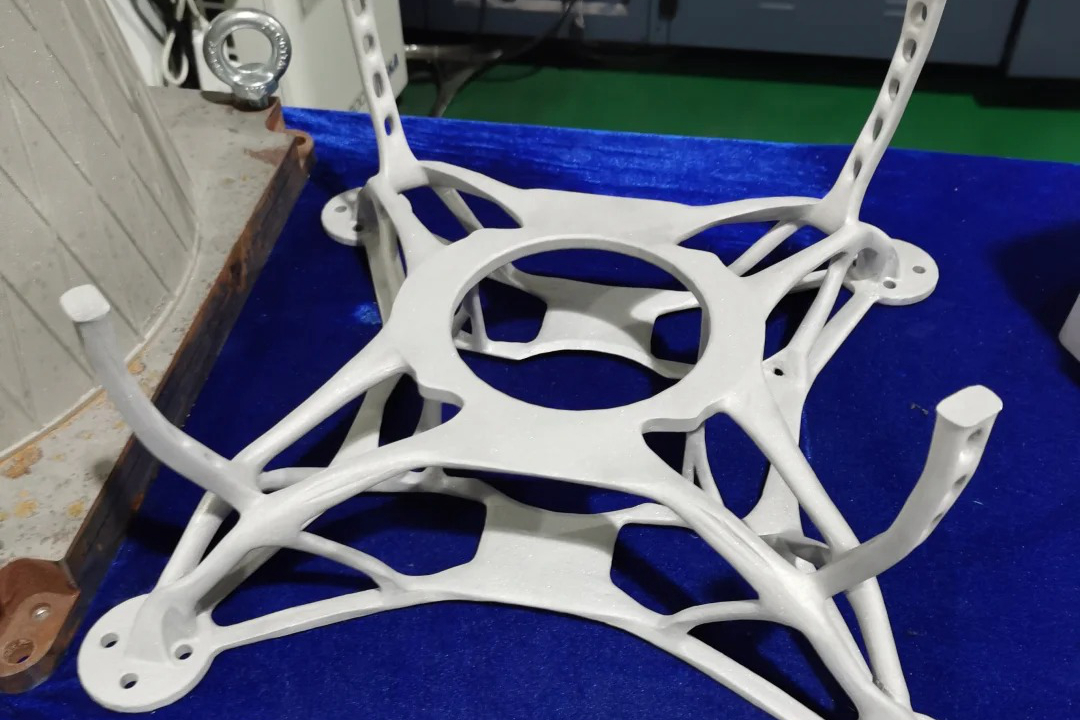
Corrax (CX) is a premium precipitation-hardening stainless tool steel specifically developed for advanced mold-making, tooling, and high-performance industrial components. In additive manufacturing, Corrax offers a powerful combination of high hardness, excellent dimensional stability, and superior corrosion resistance—qualities that are rarely found in conventional tool steels. When processed with Neway AeroTech’s high-precision stainless steel 3D printing, CX offers consistent microstructural uniformity and exceptional mechanical stability, making it especially suitable for injection molds, complex cooling channels, high-wear mechanisms, and corrosive operating environments. Its ability to achieve high hardness after aging treatment allows designers to produce functional, production-grade tooling directly from powder bed fusion without post-machining distortion. Corrax enhances reliability, improves surface quality, and increases tool life in demanding industrial applications.
International Names or Representative Grades
Region | Common Name | Representative Grades |
|---|---|---|
USA | Corrax Tool Steel | Corrax (CX) |
Europe | PH Stainless Tool Steel | CX |
China | Corrosion-Resistant Tool Steel | CX |
Japan | High-Hardness Stainless Steel | CX |
Mold Industry | Precipitation-Hardening Tool Steel | CX |
Alternative Material Options
Depending on tool performance requirements, several alternative materials may be selected. For general-purpose tooling with high wear resistance, maraging steel such as 18Ni300 provides excellent strength and machinability. For components requiring superior corrosion resistance with moderate hardness, stainless steel options such as 17-4 PH or 316L deliver improved toughness and chemical stability. In high-temperature applications, nickel-based alloys such as Inconel 625 or Inconel 718 provide excellent creep and oxidation resistance. For extreme wear conditions in harsh mechanical environments, cobalt-based solutions such as Stellite 6 offer unmatched wear and galling resistance. These alternatives enable engineers to select the optimal balance of hardness, corrosion resistance, thermal performance, and cost.
Design Purpose
Corrax was originally engineered to provide a stainless tool steel capable of achieving high hardness (up to 50+ HRC), minimal distortion, and corrosion resistance superior to traditional tool steels. Its precipitation-hardening mechanism ensures stable heat-treatment performance without excessive dimensional change, making it ideal for precision molds and long-life tooling. In additive manufacturing, Corrax is further optimized to support complex cooling channels, intricate mold geometries, and rapid production cycles, enabling mold engineers to reduce lead times while enhancing cooling efficiency and service life.
Chemical Composition (Typical)
Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
Iron (Fe) | Balance |
Chromium (Cr) | 12 |
Nickel (Ni) | 9 |
Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.4 |
Aluminum (Al) | 1.6 |
Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.5 |
Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.03 |
Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 0.5 |
Physical Properties
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Density | ~7.7 g/cm³ |
Thermal Conductivity | ~18 W/m·K |
Specific Heat | ~460 J/kg·K |
Electrical Resistivity | ~0.8 μΩ·m |
Aging Temperature Range | 425–625°C |
Mechanical Properties
Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
Tensile Strength | 1100–1400 MPa |
Yield Strength | 900–1150 MPa |
Hardness (after aging) | 42–50+ HRC |
Elongation | 8–12% |
Impact Toughness | High for tool steels |
Key Material Characteristics
Capable of achieving high hardness through controlled aging treatment
Outstanding corrosion resistance compared to conventional mold steels
Excellent dimensional stability with minimal distortion after heat treatment
High toughness suitable for long-life mold inserts and tooling components
Superior surface finish achievable through polishing and machining
Excellent printability with consistent microstructure
Supports complex cooling channel design for injection mold optimization
Stable mechanical properties across a broad temperature range
Predictable aging response for precise hardness control
Reduced maintenance requirements compared to non-stainless mold steels
Manufacturability in Different Processes
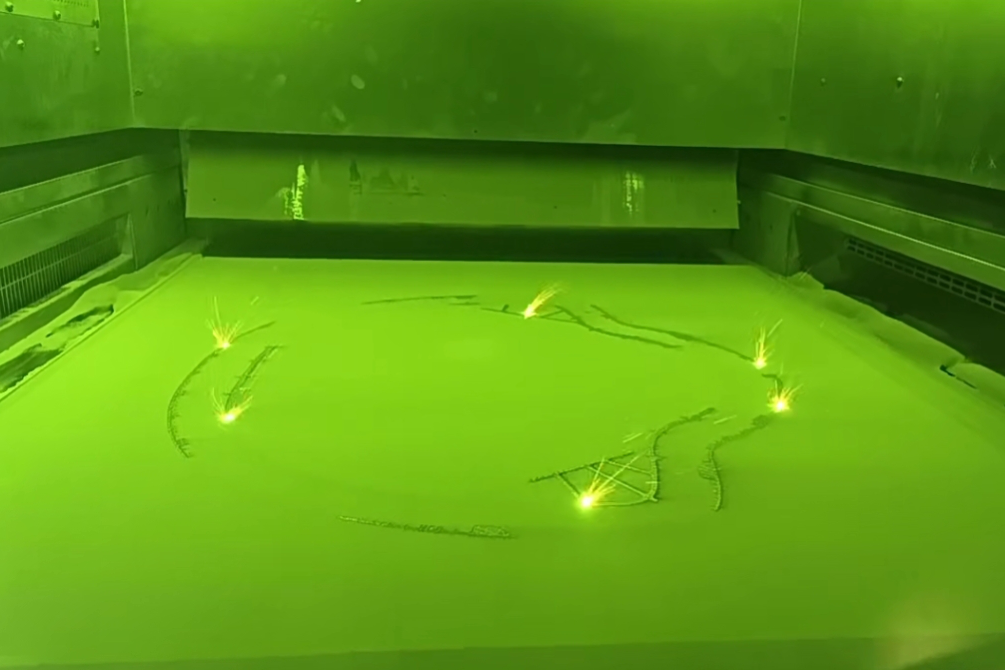
Additive manufacturing: Powder bed fusion enables high-density, production-grade tooling with optimized internal cooling structures using stainless steel 3D printing.
CNC machining: Corrax machines cleanly in the solution-treated state and is compatible with high-precision finishing supported by superalloy CNC machining.
EDM: Excellent performance in fine-detail processing through superalloy EDM.
Deep hole drilling: Complex channels and mold circuits can be refined using deep hole drilling.
Heat treatment: Corrax responds to aging cycles with predictable increases in hardness, utilizing superalloy heat treatment.
Welding: Repair or modification welding is supported under controlled conditions using superalloy welding.
Casting: Not conventionally used in casting, but underlying metallurgical principles align with precision-steel processing.
Suitable Post-Processing Methods
Aging treatment for hardness tuning and structural strengthening
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) via HIP technology to enhance density and fatigue resistance
Polishing processes to reach mold-grade surface finishes
Machining adjustments for dimensional accuracy in critical tooling components
Surface grinding and finishing for wear-sensitive surfaces
Non-destructive evaluation using advanced material testing
Cleaning and smoothing for internal mold cooling channels
Common Industries and Applications
Injection mold inserts and complex cooling molds
High-wear tooling and precision mold cores
Plastic molding systems requiring corrosion resistance
Packaging, consumer electronics, and automotive tooling
Long-life mold components for chemically aggressive polymers
Precision mechanical components requiring high hardness and low corrosion risk
When to Choose This Material
When mold components require high hardness and corrosion resistance simultaneously
When minimizing distortion during heat treatment is critical
When designing molds with conformal cooling channels optimized through additive manufacturing
When extended tooling life is required in corrosive plastic processing environments
When rapid prototyping of functional mold inserts is needed
When dimensional stability and consistent hardness are required for precision operations
When polishing quality and surface finish are essential for mold performance
When maintenance-free and durable tooling is preferred over conventional tool steels



