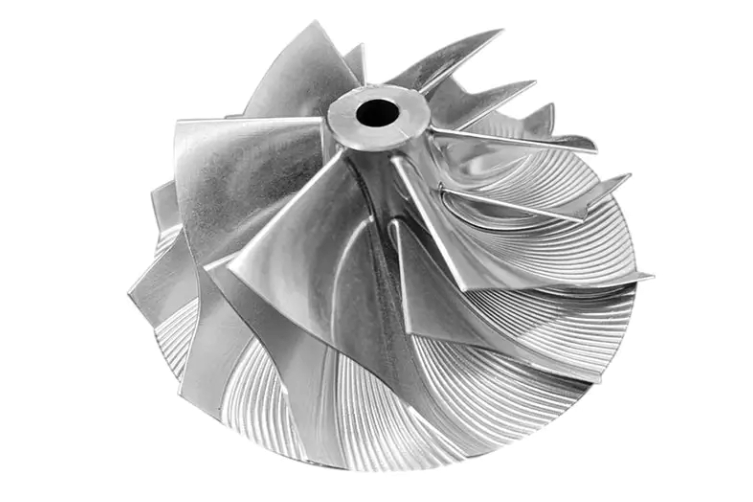
Ti-6Al-4V TC4 Turbocharger Wheels 3D Printing Manufacturer
Introduction
Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) is a titanium alloy offering a superior combination of high strength (~900 MPa), low density (4.43 g/cm³), excellent corrosion resistance, and outstanding fatigue performance. It is widely regarded as the premier material for high-speed, high-temperature turbocharger wheels in automotive, aerospace, and industrial turbo machinery.
At Neway AeroTech, we specialize in 3D printing Ti-6Al-4V turbocharger wheels using Selective Laser Melting (SLM) technology, delivering near-net-shape components with excellent mechanical properties, precise geometries, and enhanced design flexibility for maximum turbocharger efficiency.
Key Manufacturing Challenges for Ti-6Al-4V Turbocharger Wheels
Maintaining chemical composition (Al 5.5–6.75%, V 3.5–4.5%) for optimum mechanical performance.
Controlling microstructure to achieve fully dense parts with fine α+β phases for fatigue strength.
Achieving dimensional tolerances within ±0.05 mm for high-speed rotor balancing.
Ensuring surface finishes (Ra ≤5 µm as-built, Ra ≤1.6 µm after post-processing) for aerodynamic performance.
3D Printing Process for Ti-6Al-4V Turbocharger Wheels
The advanced SLM manufacturing process includes:
CAD Modeling and Simulation: Designing high-efficiency wheel geometries with lightweight optimization.
Powder Layering and Laser Melting: Ti-6Al-4V powder layer-by-layer fusion at ~1600°C under inert gas atmosphere.
Support Structure Removal: Post-build removal of supports to minimize internal stresses.
Heat Treatment (Annealing): Conducted at ~800°C–950°C to refine microstructure and relieve residual stresses.
Precision CNC Machining: Final critical surface finishing to achieve tight tolerances and smooth aerodynamic surfaces.
Comparative Analysis of Manufacturing Methods for Turbo Wheels
Process | Surface Finish | Dimensional Precision | Mechanical Properties | Design Flexibility | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SLM 3D Printing + Machining | Good to Excellent (Ra ≤1.6 µm) | Very High (±0.05 mm) | Excellent (~900 MPa) | Outstanding | High for small batches |
Investment Casting | Good (Ra ~3–5 µm) | Moderate (±0.2 mm) | Very Good (~860 MPa) | Limited | Low for large batches |
Forging + Machining | Excellent (Ra ≤0.8 µm) | Very High (±0.01 mm) | Superior (~950 MPa) | Low | High |
Optimal Manufacturing Strategy for Ti-6Al-4V Turbo Wheels
SLM 3D printing: Best for highly complex, lightweight-optimized turbocharger wheel designs requiring tight tolerances and superior performance.
Investment casting: Suitable for simpler, thicker-walled geometries in high-volume production.
Forging + CNC machining: Best for applications requiring extremely high mechanical strength but less design flexibility.
Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) Alloy Performance Overview
Property | Value | Application Relevance |
|---|---|---|
Tensile Strength | ~900 MPa | High-speed turbine wheel durability |
Yield Strength | ~830 MPa | Maintains strength under high centrifugal forces |
Density | 4.43 g/cm³ | Lightweight design, improving spool-up response |
Fatigue Strength | ~510 MPa | Critical for long-term high-speed rotation |
Maximum Operating Temperature | ~400°C | Withstands elevated temperatures in turbo environments |
Advantages of Using Ti-6Al-4V for Turbocharger Wheels
High strength-to-weight ratio enhances turbocharger acceleration and reduces inertia.
Excellent corrosion resistance protects against hot gases and combustion byproducts.
Outstanding fatigue resistance extends service life under extreme cyclic loading.
Superior design freedom enables manufacturing of optimized, hollow, or integrated geometries.
Post-processing Techniques for Ti-6Al-4V Turbocharger Wheels
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Densifies the structure by eliminating residual porosity, improving fatigue life by 20–30%.
Heat Treatment (Annealing): Refines α+β phase microstructure for balanced strength and ductility.
Precision CNC Machining: Achieves final tolerances within ±0.01 mm and aerodynamic surface smoothness (Ra ≤0.8 µm).
Surface Finishing (Polishing/Shot Peening): Enhances fatigue life and reduces surface roughness for improved gas flow.
Inspection and Quality Assurance for Turbocharger Wheels
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): Measures critical aerodynamic profiles to ±0.01 mm accuracy.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning: Detects internal porosity or defects non-destructively.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Evaluates internal quality to aerospace standards.
Dye Penetrant Testing (PT): Identifies fine surface cracks as small as 0.002 mm.
Industry Applications and Case Study
Ti-6Al-4V turbocharger wheels manufactured by Neway AeroTech are widely used in high-performance automotive turbochargers, aerospace auxiliary power units (APUs), and industrial high-speed turbo compressors. In a competitive motorsport program, our 3D-printed Ti-6Al-4V wheels improved spool-up times by 18% and demonstrated 25% higher fatigue life compared to traditional aluminum turbine wheels.
FAQs
What dimensional tolerances can Neway AeroTech achieve for Ti-6Al-4V turbocharger wheels?
Why is SLM 3D printing preferred for complex turbocharger wheel designs?
How does Ti-6Al-4V compare to aluminum alloys for turbocharger applications?
What post-processing steps are critical for Ti-6Al-4V turbo wheels?
How does Neway AeroTech ensure the quality and durability of 3D-printed turbocharger wheels?