Essential Tests for Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Quality on Superalloy Castings
Key Tests for Evaluating Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Quality on Superalloy Castings
Evaluating the quality of a Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) system is critical for ensuring the performance and longevity of high-temperature components like turbine blades and vanes. A multi-faceted testing approach is required to assess the coating's mechanical integrity, thermal performance, and microstructural soundness before it enters service.
Adhesion and Cohesion Strength Testing
The most fundamental test is evaluating the coating's bond strength to the superalloy substrate, typically a part produced via vacuum investment casting. The standard method is tensile adhesion testing (e.g., ASTM C633), which pulls a stub glued to the coating surface until failure occurs. The failure mode—whether within the glue, the ceramic topcoat, the bond coat, or at the interface—is more informative than the pure strength value. A cohesive failure within the topcoat is often acceptable, while adhesive failure at the bond coat interface indicates poor preparation or processing.
Thickness and Uniformity Measurement
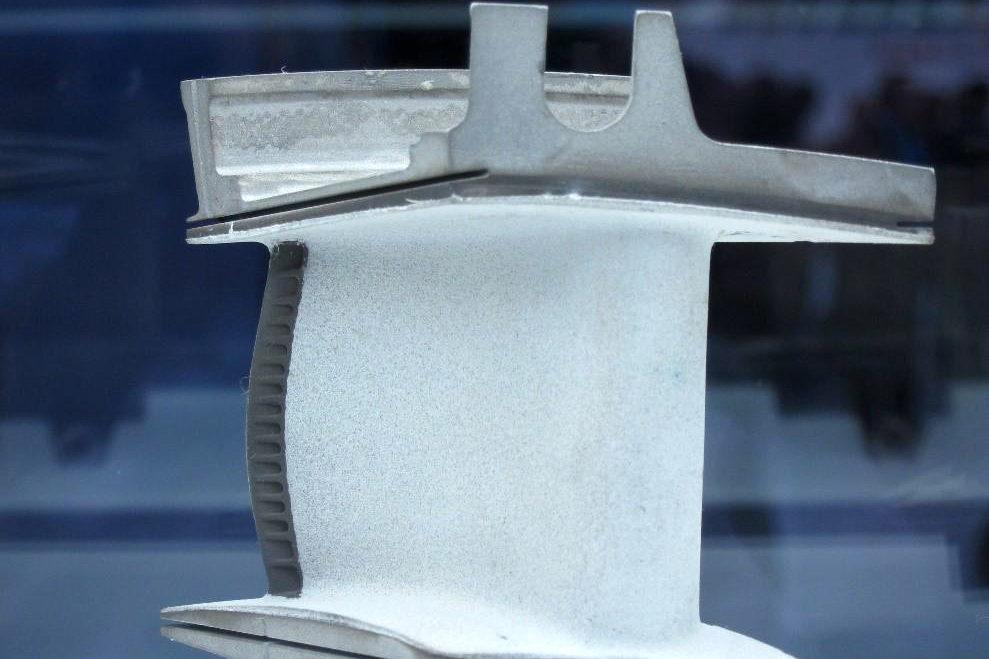
Coating thickness must be tightly controlled and uniform across the complex geometry of a casting. Non-destructive techniques like eddy current testing are used to measure the conductive bond coat thickness, while ultrasonic gauges can measure the total TBC system thickness. Metallographic cross-sectioning is the definitive destructive method, allowing for precise measurement of both the ceramic topcoat and the thermally grown oxide (TGO) layer under a microscope. This is crucial for components from single crystal casting, where coating uniformity directly affects part life.
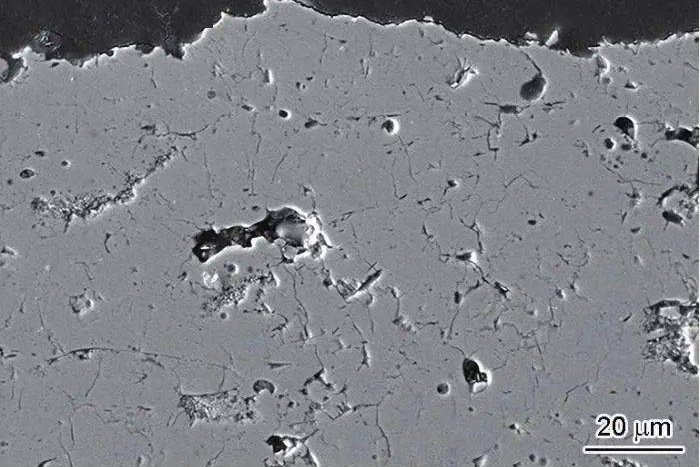
Microstructural Analysis
Cross-sectional analysis using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is indispensable. It reveals critical microstructural features such as: * Porosity and crack networks within the ceramic layer, which affect strain tolerance and thermal conductivity. * The integrity and thickness of the TGO (alumina layer) between the bond coat and topcoat. A thin, continuous TGO is desirable; a thick or irregular TGO is a precursor to spallation. * The presence of unwanted phases or contaminants. This level of material testing and analysis validates the coating process and predicts performance.
Thermal Cyclic and Burner Rig Testing
Laboratory tests simulate service conditions. Thermal cyclic testing involves repeatedly heating the coated specimen to high temperature in a furnace and then cooling it rapidly. Burner rig testing is more advanced, exposing the coating to a high-velocity flame, simulating the thermal gradients and heat fluxes of a real engine. Both tests measure the number of cycles to failure (coating spallation), providing accelerated life data that is correlated to performance in aerospace and aviation applications.
Composition and Phase Analysis
Techniques like Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) are used to verify the chemical composition of the coating layers and identify the crystalline phases present. This confirms the correct application of the bond coat (typically MCrAlY) and ensures the ceramic topcoat is in the desired metastable tetragonal prime (t') phase for optimal performance.
Non-Destructive Inspection (NDI) for Defects
Finally, 100% of production components undergo NDI. Thermography (IR imaging) can detect disbonds and delaminations by analyzing heat flow through the coating. High-sensitivity ultrasonic C-scan can also map the integrity of the coating-substrate bond, ensuring no large-scale defects are present before a critical part, such as one destined for power generation, is shipped.