What is the importance of post-processing in superalloy manufacturing?
Role of Post-Processing in Superalloy Manufacturing
Post-processing is essential to transform as-cast or as-printed superalloy components into high-performance parts capable of operating under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. Whether components are produced by vacuum investment casting or superalloy 3D printing, initial manufacturing inevitably introduces defects such as microshrinkage, internal porosity, surface roughness, and non-uniform microstructures. Post-processing eliminates these weaknesses and ensures that the final part meets aerospace, energy, or defense-grade reliability standards.
The post-processing route depends on the application, alloy grade, and operating environment. Processes such as heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) optimize microstructure and eliminate porosity, while superalloy CNC machining restores dimensional accuracy and surface finish for assembly.
Microstructural Optimization and Defect Removal
For advanced nickel and cobalt-based alloys such as Inconel 738 or Stellite 6, post-processing controls phase precipitation, improves grain boundary cohesion, and enhances creep resistance. HIP specifically addresses internal voids that would otherwise act as crack initiation points, whereas heat treatment adjusts γ′/γ″ precipitation for high-temperature strength retention.
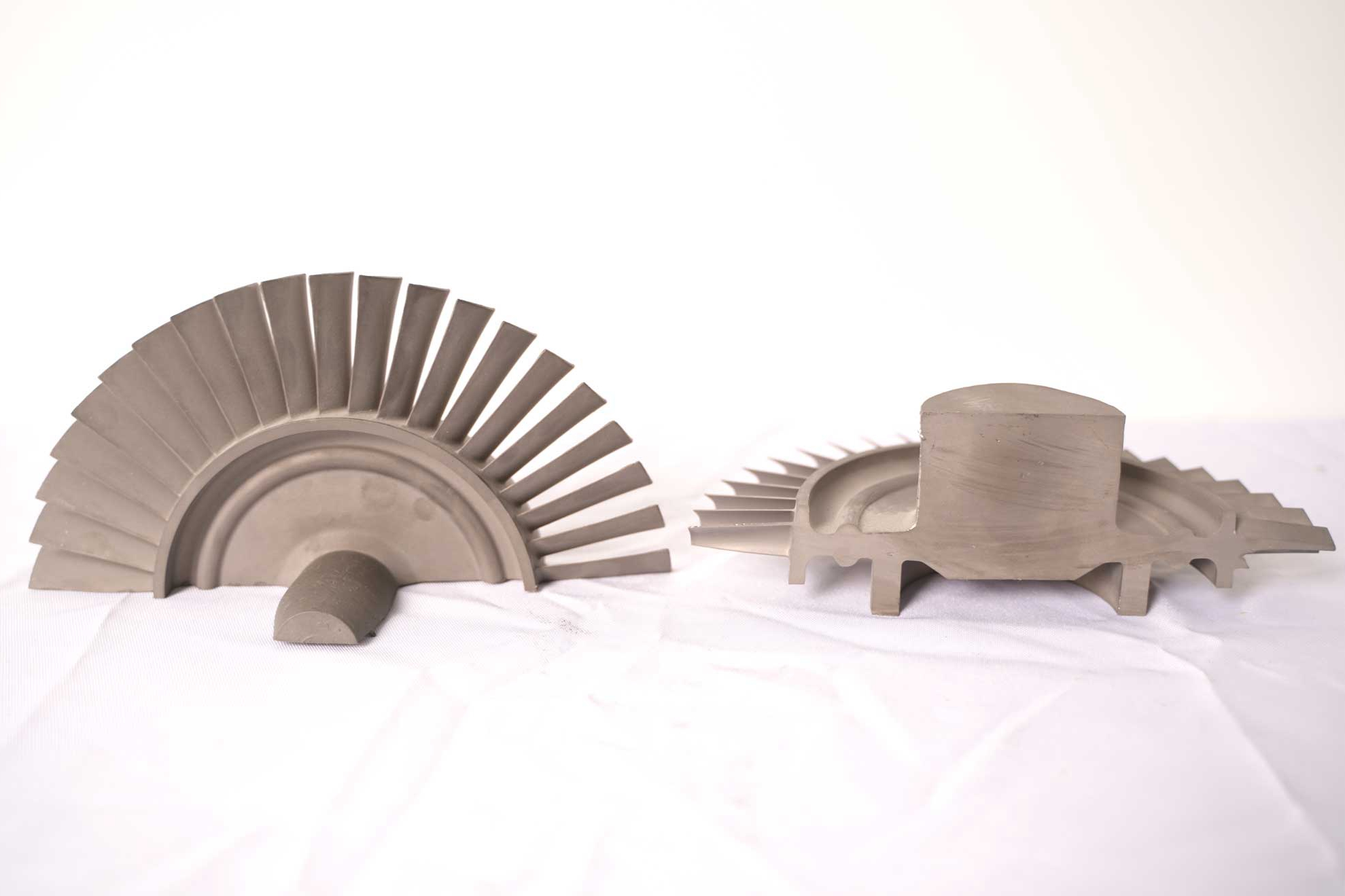
In high-performance turbine blades from third-generation single crystal casting, precise post-processing ensures directional grain orientation remains intact while preventing stress concentration. Without proper post-processing, even a well-cast component may fail prematurely in service due to thermal fatigue or oxidation.
Surface Enhancement and Functionality
Post-processing also improves surface functionality, corrosion resistance, and wear behavior. Techniques such as thermal barrier coating (TBC) and superalloy welding provide thermal insulation and structural reinforcement in critical zones. For rotating or flow-control components in chemical processing and nuclear systems, precise surface finishing prevents leakage, galling, and chemical degradation.
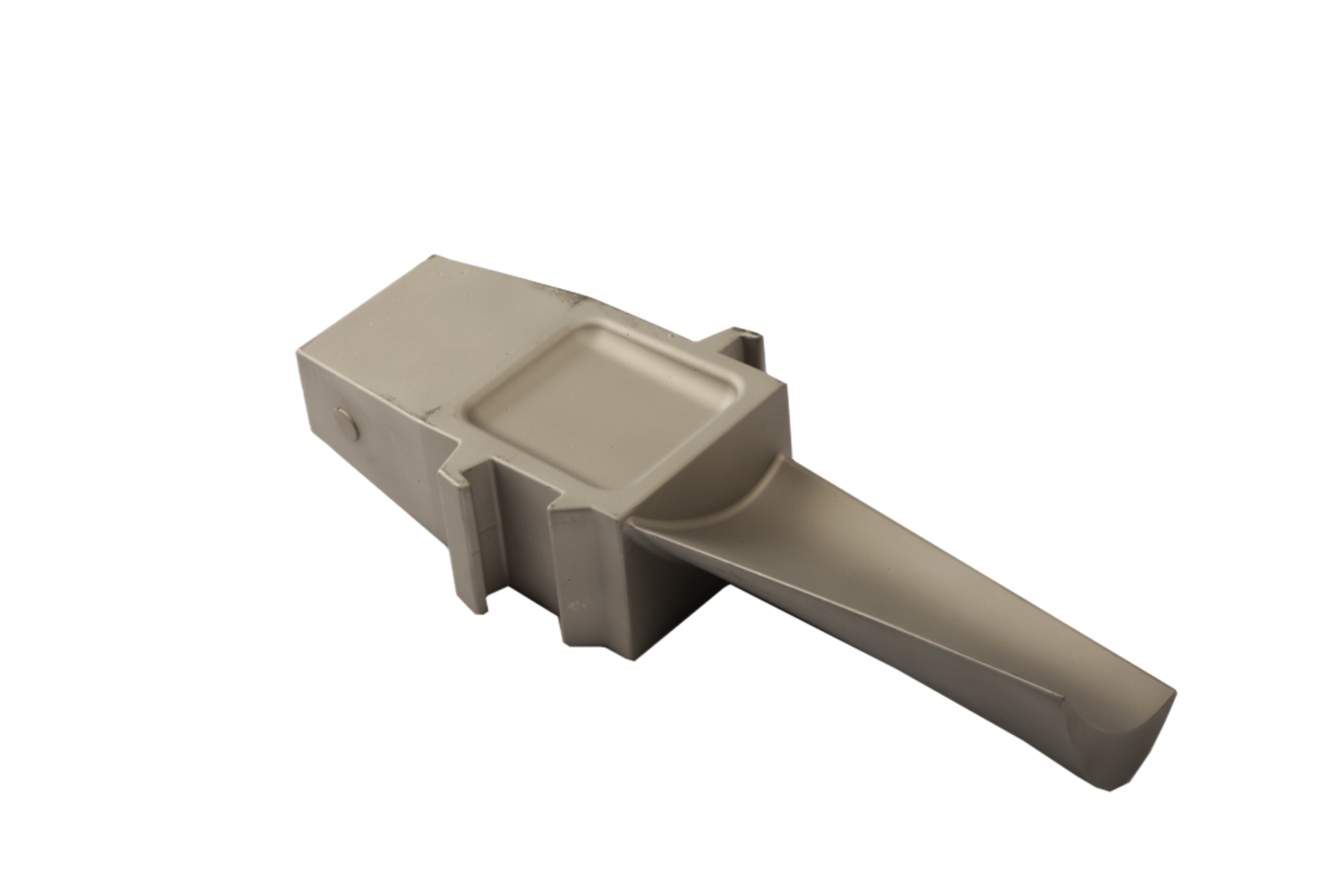
Additionally, superalloy deep hole drilling and EDM machining allow engineers to fabricate cooling channels and intricate geometries impossible to achieve during primary casting.
Quality Verification
To guarantee performance, strict material testing and analysis confirm the success of each post-processing step. X-ray scanning, CT inspection, and metallography validate internal structure, while tensile, creep, and fatigue tests ensure compliance with aerospace or defense specifications. Only after comprehensive verification can a superalloy component be approved for use in real-world, high-stress environments.