Electropolishing for Aerospace: Enhancing Corrosion Resistance & Surface Integrity
Electropolishing for Aerospace Corrosion Resistance
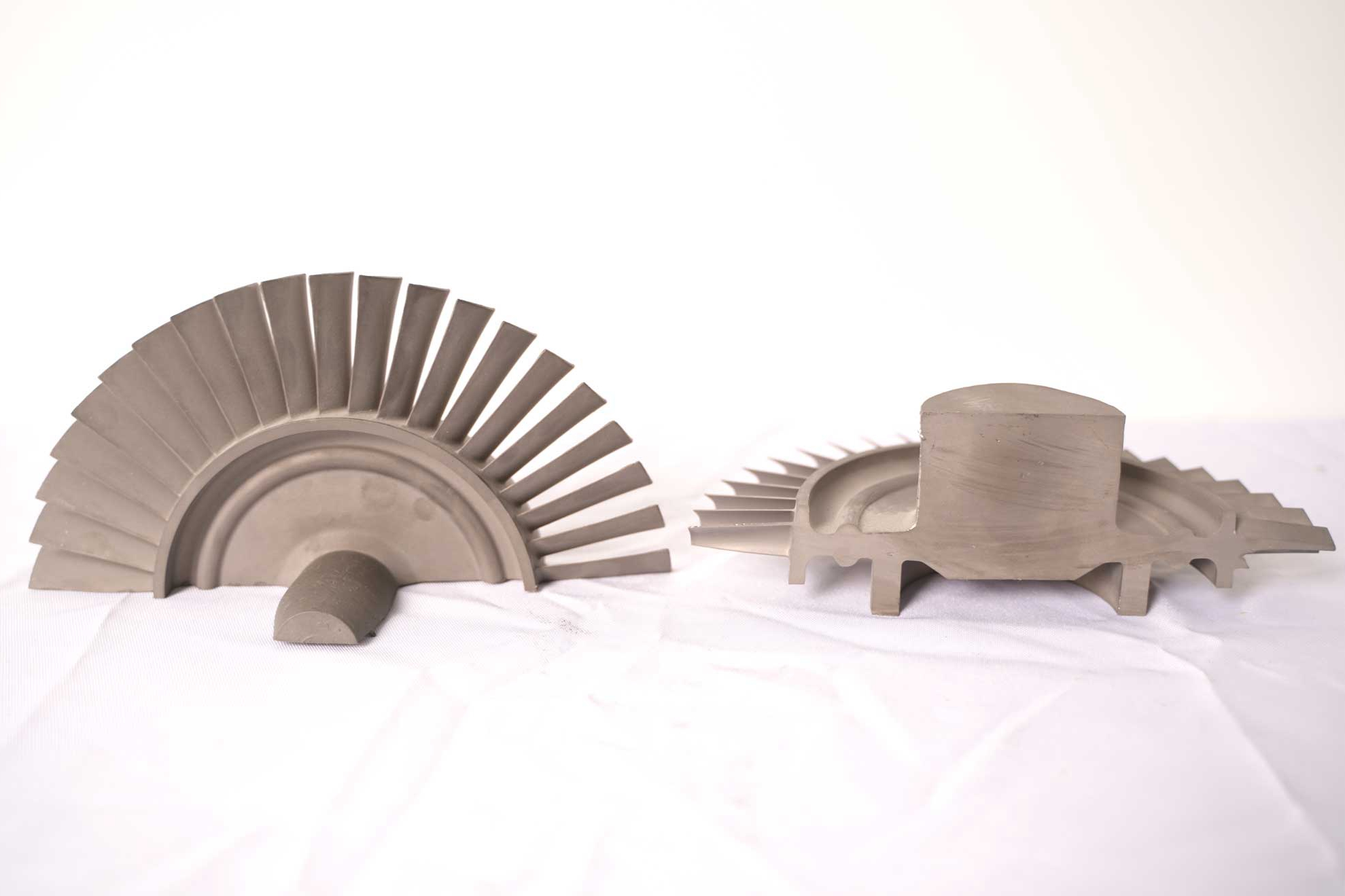
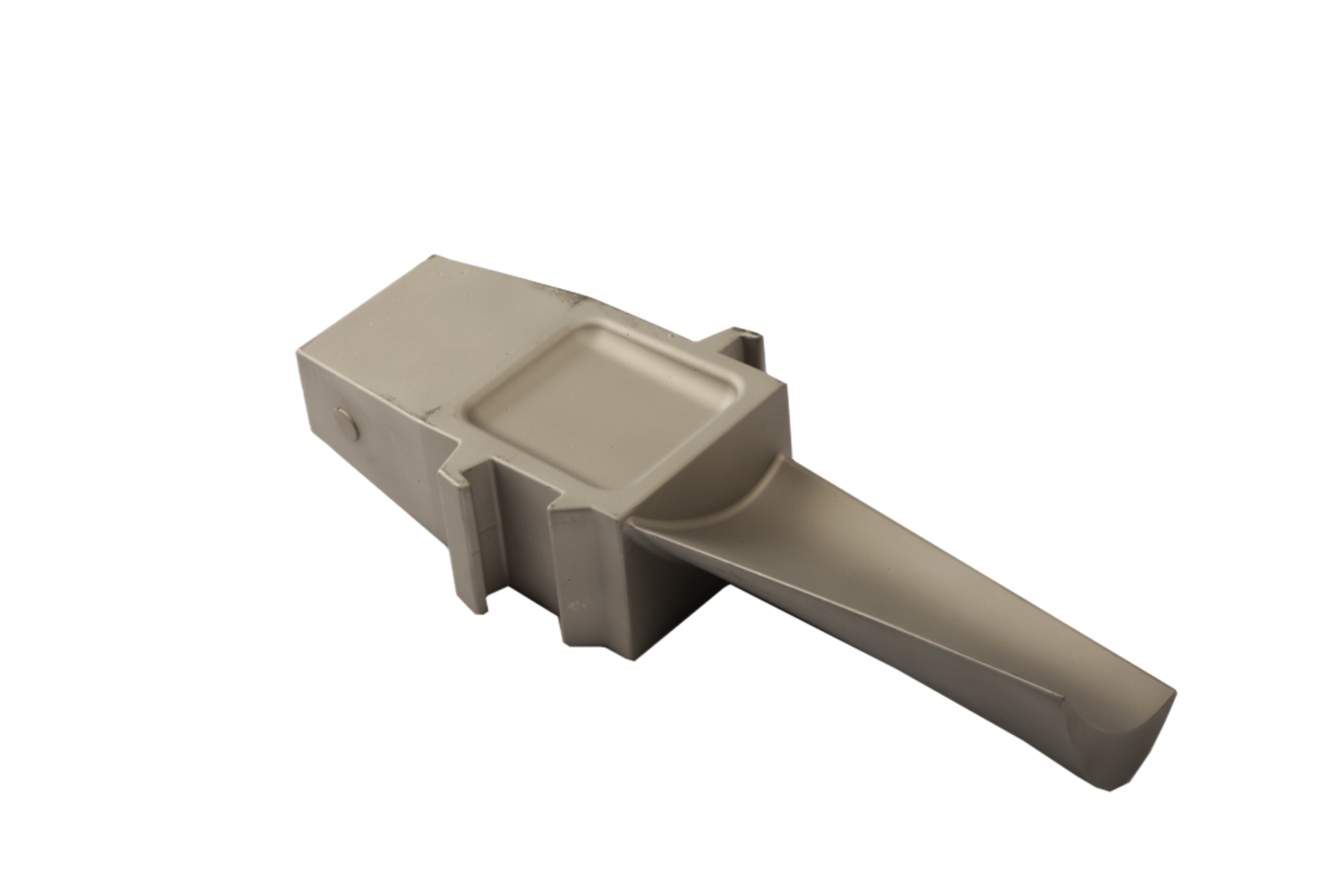
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that selectively removes surface material from a metal component, resulting in a smooth, mirror-like finish with enhanced corrosion resistance, deburred edges, and micro-crack-free surface. It serves as a critical final finishing step for aerospace components, directly addressing the industry's stringent requirements for reliability and longevity in harsh environments.
The Electropolishing Process Explained
During electropolishing, the component acts as an anode submerged in a temperature-controlled electrolyte bath. When an electrical current is applied, ions are removed from the surface, leveling microscopic peaks and valleys.
Anodic Leveling: The process preferentially dissolves microscopic high points, burrs, and asperities, creating a smoother surface profile.
Smoothening: It reduces surface roughness to a very low Ra value, eliminating sites where corrosive agents can accumulate.
This process is often a key part of the final post-process finishing for components before they enter service.
How It Enhances Aerospace Corrosion Resistance
The improvement in corrosion resistance is achieved through several simultaneous mechanisms:
Creation of a Passive Oxide Layer: Electropolishing promotes the formation of a uniform, dense, and chemically stable passive layer (e.g., chromium oxide on stainless steels or superalloys). This layer acts as a highly effective barrier against oxidants and chlorides encountered in aerospace and aviation environments, such as marine atmospheres and de-icing salts.
Elimination of Surface Defects: By removing "feathers," micro-burrs, and embedded impurities from prior CNC machining or welding, electropolishing eliminates microscopic initiation sites for pitting and crevice corrosion. A pit that cannot start will not propagate.
Reduction of Surface Area: A smoother surface has less total area exposed to the corrosive environment, directly reducing the rate of corrosive attack.
Removal of Surface Contamination: The process strips away residual iron particles and other contaminants introduced during fabrication that can create galvanic cells and initiate rust.
Synergy with Other Aerospace Manufacturing Processes
Electropolishing is often used in conjunction with other critical processes to maximize component life:
Post-HIP and Heat Treatment: After processes like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and heat treatment, components may have a thermally oxidized scale or slight discoloration. Electropolishing cleans and refines this surface, ensuring optimal quality before the application of a Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC).
Improved Coating Adhesion: The ultra-clean and microscopically smooth surface provided by electropolishing offers a superior substrate for coatings, preventing under-coating corrosion and spallation.
Additional Aerospace-Specific Benefits
Beyond corrosion resistance, electropolishing offers other critical advantages:
Fatigue Life Enhancement: By removing stress concentrators like micro-notches and scratches, it can improve the component's resistance to fatigue crack initiation.
Hygienic and Cleanable Surface: The non-stick, easy-clean surface is vital for fuel systems, hydraulic components, and parts used in pharmaceutical and food processing applications within the aerospace sector (e.g., galley equipment).
Deburring of Complex Internal Passages: It can effectively deburr intricate internal channels in fuel nozzles and manifolds that are inaccessible to mechanical methods, preventing debris-related failures.
In summary, electropolishing is not merely a cosmetic treatment but a vital surface engineering process. By fundamentally improving the surface metallurgy of components, it provides a critical line of defense against corrosion, directly contributing to the safety, reliability, and extended service life required in demanding aerospace applications.