What is Isothermal Forging of High-Temperature Alloys?
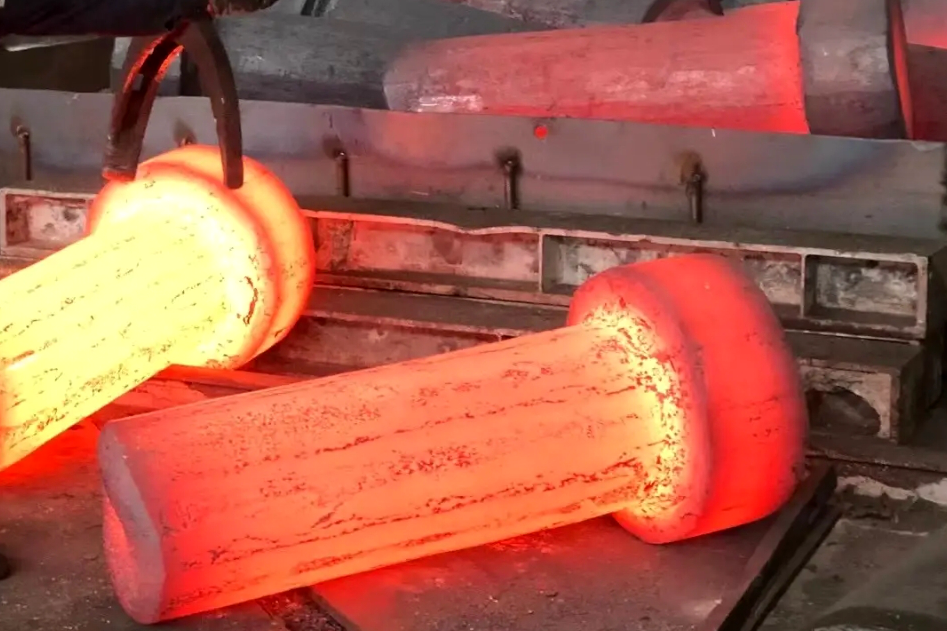
Isothermal forging is a specialized metalworking process often used to manufacture components from high-temperature alloys, such as Inconel, Hastelloy, and CMSX alloys. These alloys are commonly used in aerospace and aviation, power generation, and defense industries, where high performance under extreme conditions is required. The forging process involves shaping metals by applying heat and pressure, with isothermal forging characterized by precise temperature control. This results in parts with enhanced mechanical properties, which benefit applications in high-stress environments.
This blog will explore the isothermal forging process, its critical importance for high-temperature alloys, and how it contributes to producing high-quality components that can withstand extreme operational conditions.
The Science Behind Isothermal Forging
Isothermal forging is a highly controlled process in which the workpiece and the die are maintained at the same elevated temperature throughout the operation. Unlike conventional forging methods, where the die temperature is lower, isothermal forging maintains uniformity, which helps reduce defects like strain and cracks. The consistent temperature control ensures the alloy remains in a superplastic state, allowing for significant deformation without cracking and resulting in precise shapes and excellent surface finishes.
This forging technique benefits high-temperature alloys, producing components with exceptional strength, durability, and fatigue resistance. Isothermal forging ensures the material's integrity, making it suitable for components like turbine blades, which operate under extreme thermal and mechanical conditions.
Why Isothermal Forging for High-Temperature Alloys?
High-temperature alloys, such as Nimonic and Rene Alloys, are engineered to perform under extreme thermal and mechanical stresses. Their composition, typically rich in nickel, cobalt, and chromium, gives them excellent thermal stability and oxidation resistance. These properties make them ideal for gas turbine engines, jet engines, nuclear reactors, and other high-stress environments. However, their resistance to deformation makes conventional forging methods challenging.
With isothermal forging, the consistently high temperature keeps the alloy in a more malleable state, which prevents defects like cracking or grain size inconsistencies. This results in components with excellent creep strength and mechanical properties, making isothermal forging a preferred method for superalloy components.
The Isothermal Forging Process Step-by-Step
The isothermal forging process involves several carefully controlled steps to ensure that the final product meets the demanding requirements of high-temperature alloy applications.
1. Preparation of the Die and Alloy Materials
The process begins with preparing both the die and the alloy workpiece. The die is designed to match the exact shape of the desired component and is made from a material that can withstand high temperatures and repeated use. The workpiece is heated to a temperature suitable for its alloy, such as CMSX-4, ensuring its material properties remain consistent.
2. Heating to the Forging Temperature
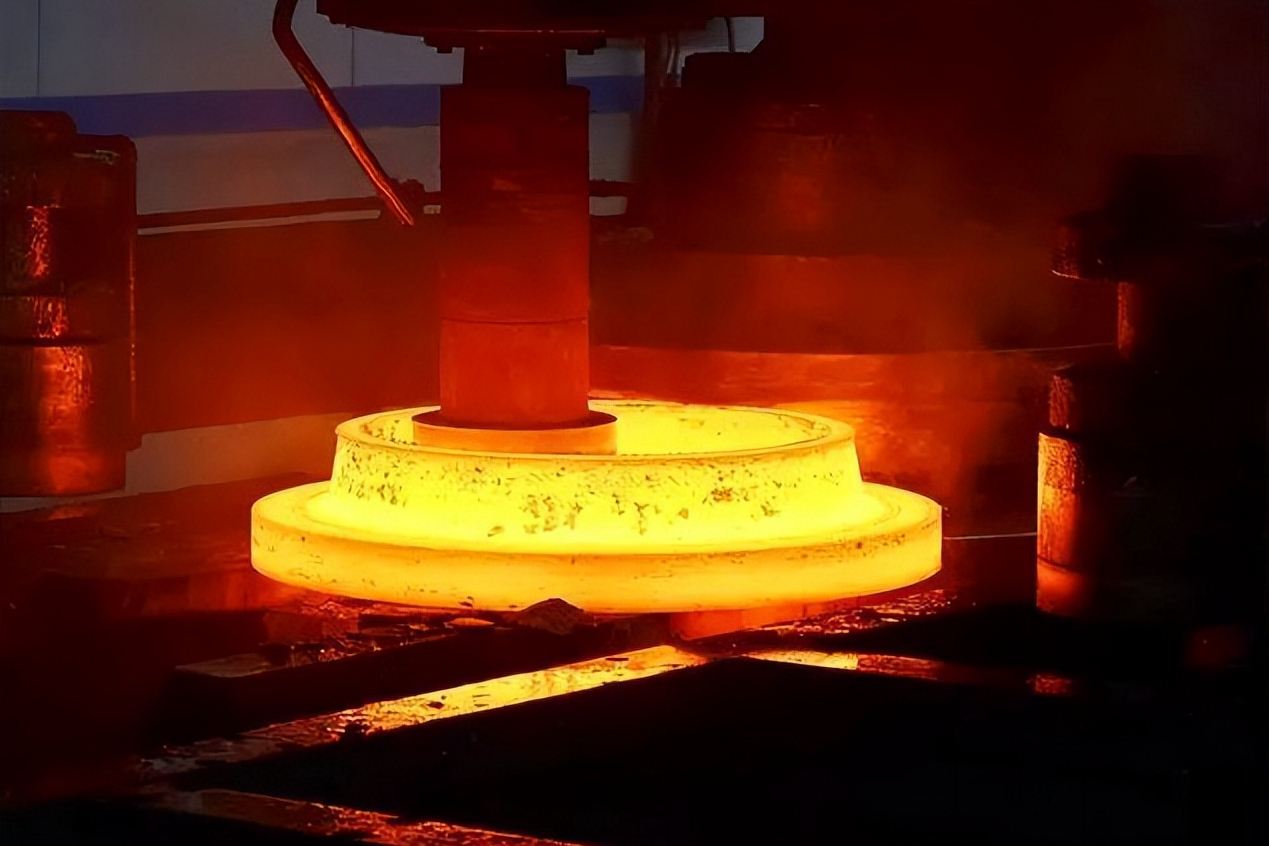
The workpiece and the die are heated to the same target temperature, ranging between 900°C to 1250°C. For example, Inconel 718 requires precise temperature maintenance, as isothermal forging ensures material uniformity and strength throughout the forging process.
3. Forging Process
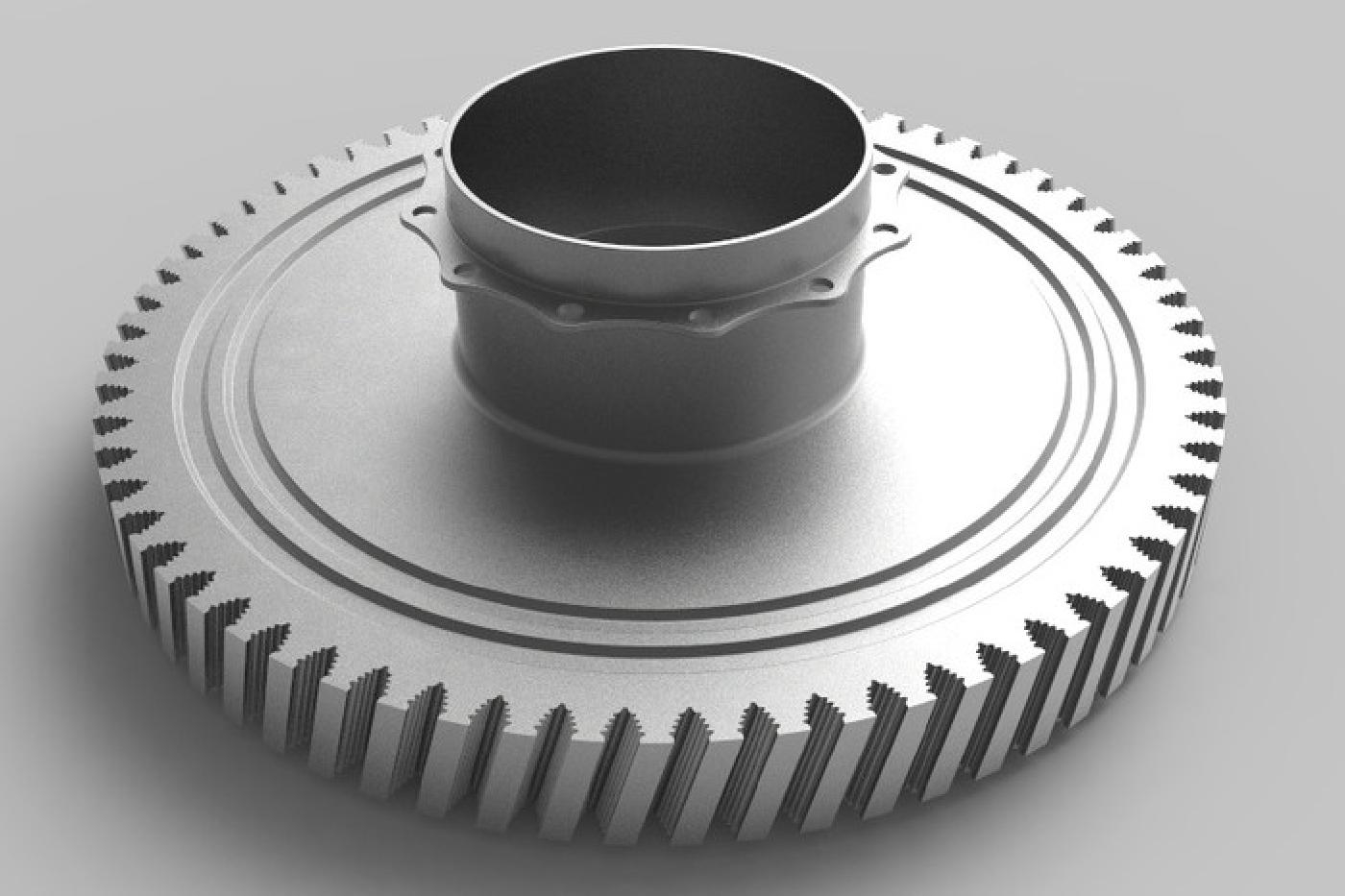
Once the components are at the target temperature, the workpiece is placed in the heated die, and pressure is applied. The isothermal forging process involves continuous pressure application, allowing the material to deform plastically without cracking. This technique ensures that the grain structure remains intact, which is vital for components such as turbine discs.
4. Cooling and Post-Forging Operations
After forging, controlled cooling is critical to maintaining the uniform grain structure of the component. Depending on the requirements, additional post-process operations, such as heat treatment or CNC machining, may be necessary to bring the component to its final specification.
Critical Advantages of Isothermal Forging
Isothermal forging offers numerous advantages for high-temperature alloy components in demanding industries.
1. Uniform Grain Structure
Maintaining a consistent temperature during forging produces a uniform grain structure, resulting in components with superior mechanical properties and enhanced fatigue resistance.
2. Reduced Defects
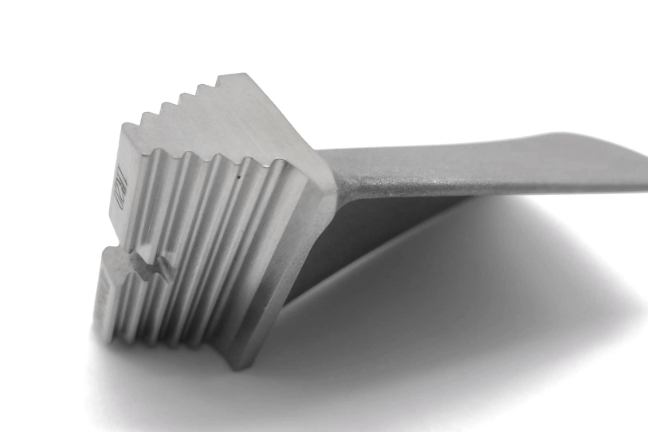
By maintaining a constant temperature, isothermal forging minimizes defects such as porosity and residual stresses. This ensures greater control over material flow and reduces imperfections in critical components, such as aerospace turbine blades.
3. Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Components forged using the isothermal process exhibit enhanced mechanical properties, including improved tensile strength and creep strength, which are vital for parts such as jet engine turbines and reactor components.
4. Complex Geometries
The superplastic state allows for the production of intricate geometries, which makes isothermal forging suitable for components with complex shapes, such as control rod mechanisms.
5. High Material Utilization
The process also yields high material utilization with minimal waste, which is particularly beneficial when working with expensive alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V (TC4).
Industries and Applications
Isothermal forging is extensively used in industries that require superior mechanical properties and high thermal resistance:
1. Aerospace and Aviation
In the aerospace industry, isothermal forging produces critical components, such as jet engine turbines and compressor blades. These components must withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses.
2. Power Generation
Gas turbines used in power generation benefit from isothermal forging due to their need for high-temperature strength. This ensures components like turbine blades can endure high-stress conditions without failure.
3. Military and Defense
The military and defense industries employ isothermal forging for components like jet engines, where reliability is paramount under extreme conditions.
4. Nuclear Energy
Isothermal forging is also used for nuclear reactor components, including reactor internals requiring strength, radiation resistance, and durability.
Challenges in Isothermal Forging
1. High Costs
The isothermal forging process involves high costs due to specialized equipment and the energy needed to maintain consistent temperatures. Equipment like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) can be expensive to operate.
2. Technical Expertise
Isothermal forging requires skilled personnel for precise temperature control and careful material handling, ensuring that the forging parameters yield high-quality components.
Technological Innovations and Future Trends
Recent advancements are addressing challenges associated with isothermal forging:
1. Simulation and Modeling
Innovations like computer simulation help optimize the forging process, providing insights into material flow and deformation, which is essential for components like Rene 80.
2. Automation and Control Systems
Automation in isothermal forging, such as automated control systems, ensures precise temperature control and force application, reducing the risk of human error.
3. Integration with Additive Manufacturing
Combining isothermal forging with additive manufacturing can create high-quality components with reduced waste. Techniques like 3D printing services can be integrated for efficiency.
Conclusion
Isothermal forging is crucial for producing high-temperature alloy components with exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to extreme thermal and mechanical conditions. Despite challenges like high costs, technological advancements are paving the way for improved efficiency and broader applications.
As innovations like simulation, automation, and integration with additive manufacturing progress, the future of isothermal forging looks promising for aerospace, power generation, defense, and nuclear energy applications.



