How is the Quality of Stainless Steel Parts Produced by SLM 3D Printing Ensured?
Systematic Quality Assurance Framework
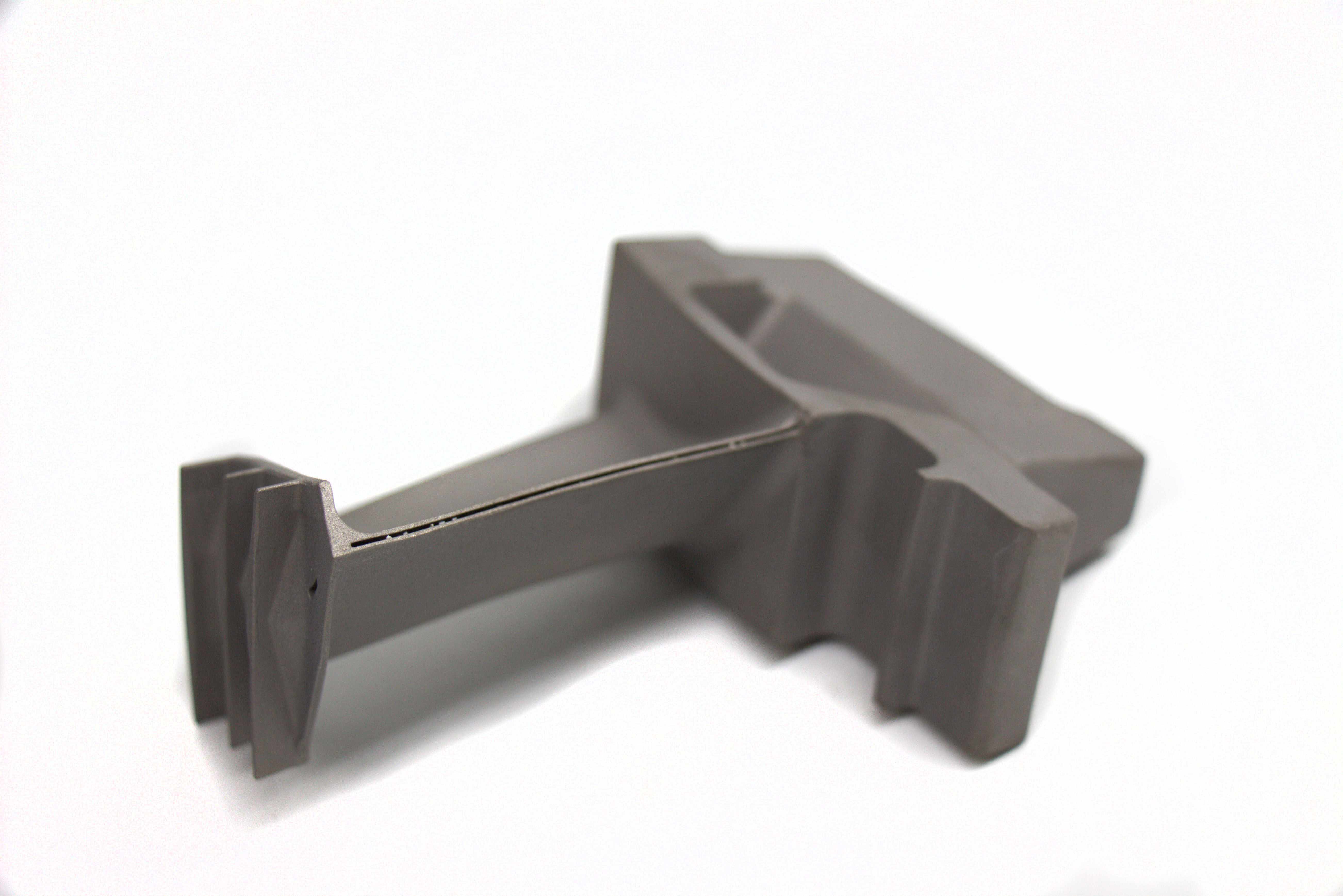
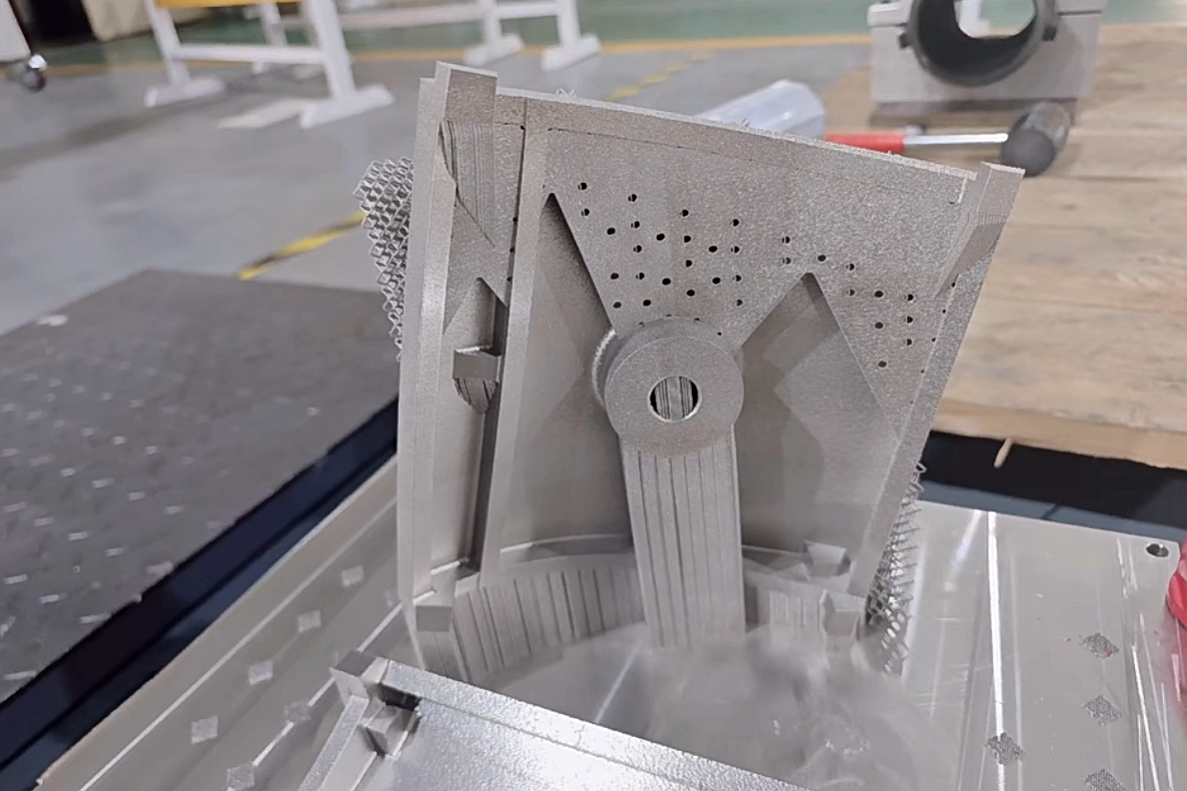
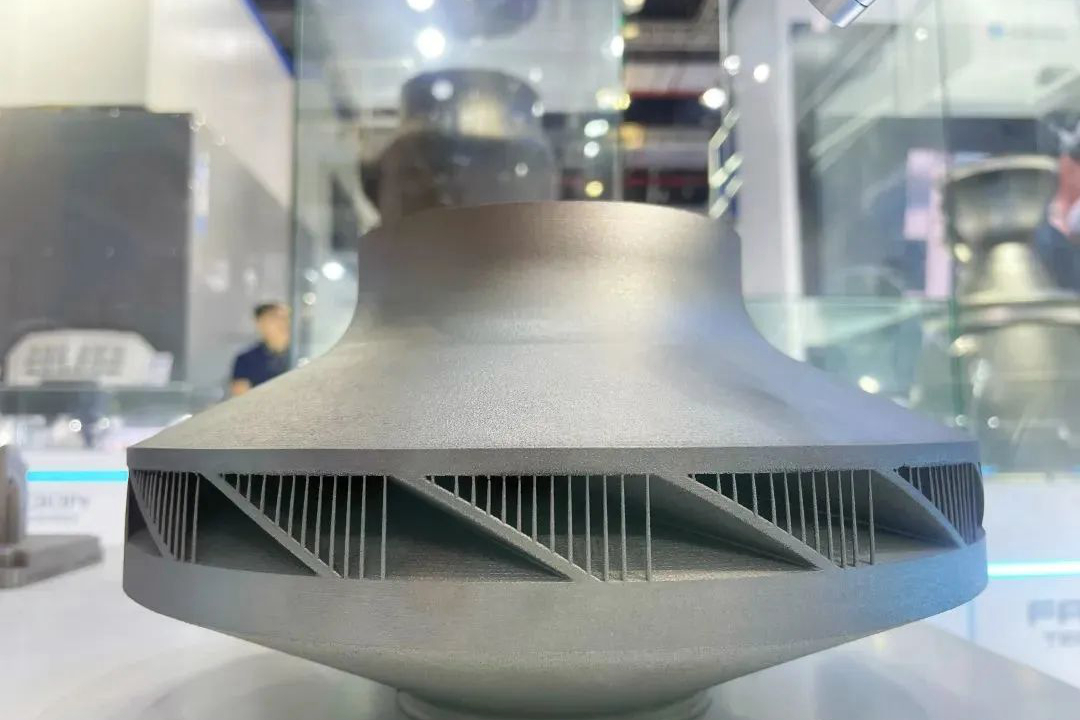
Ensuring the quality of stainless steel parts produced by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) requires a comprehensive, multi-stage framework that integrates design, process control, post-processing, and validation. Quality is not inspected into a part but is built into every step of the digital-to-physical workflow. This begins with Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) optimization to mitigate residual stress and support requirements, and extends through rigorous material testing and analysis of the final component. The assurance process is especially critical for parts destined for regulated industries like aerospace and aviation or medical.
In-Process Monitoring and Control
Real-time monitoring during the build is fundamental to quality assurance. Advanced SLM systems are equipped with sensors that track key parameters:
Melt Pool Monitoring: Optical or thermal cameras monitor the laser-powder interaction, detecting anomalies like spatter or lack-of-fusion that could lead to defects.
Layer-by-Layer Inspection: Coaxial or off-axis imaging validates the geometry of each solidified layer against the digital slice, identifying any significant deviations early.
Atmosphere & Parameter Stability: The integrity of the inert argon or nitrogen atmosphere and the consistency of laser power, speed, and scanning strategy are continuously logged to ensure a stable, repeatable process.
This data-driven approach allows for traceability and the early identification of process drifts that could affect material properties in grades like 316L.
Post-Process Densification and Treatment
As-built SLM parts contain inherent characteristics that must be addressed to ensure service-quality performance. Standard post-processes include:
Stress Relief & Heat Treatment: To eliminate residual stresses and tailor mechanical properties (e.g., hardening 17-4 PH via aging).
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): For critical components, HIP is applied to close internal micro-porosity, achieving near-theoretical density and dramatically enhancing fatigue life and ductility.
Precision Machining: Critical interfaces and toleranced features are finished using CNC machining to meet exact dimensional specifications.
Comprehensive Validation and Inspection
Final quality is verified through a battery of destructive and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods:
Dimensional Metrology: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and laser scanners verify part geometry against the original CAD model.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like dye penetrant testing (PT), X-ray computed tomography (CT scanning), and ultrasonic testing inspect for surface and internal defects without damaging the part.
Mechanical & Microstructural Testing: Coupons built alongside the production parts are subjected to tensile, fatigue, hardness, and corrosion tests. Metallographic analysis confirms the microstructure is free of unexpected phases or defects, validating the entire process chain from powder to final part.