How does the choice of bond coat affect the overall performance of the TBC system?
Role of Bond Coat in TBC Performance
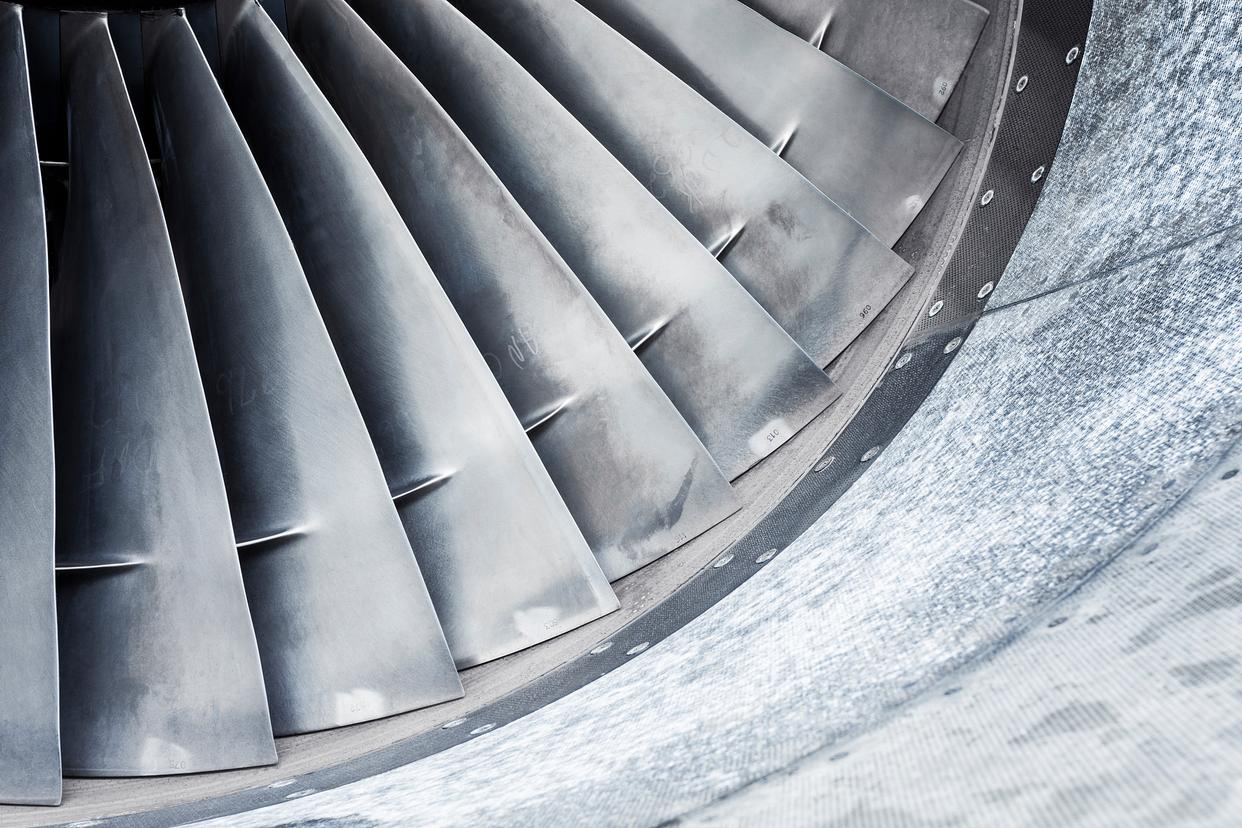
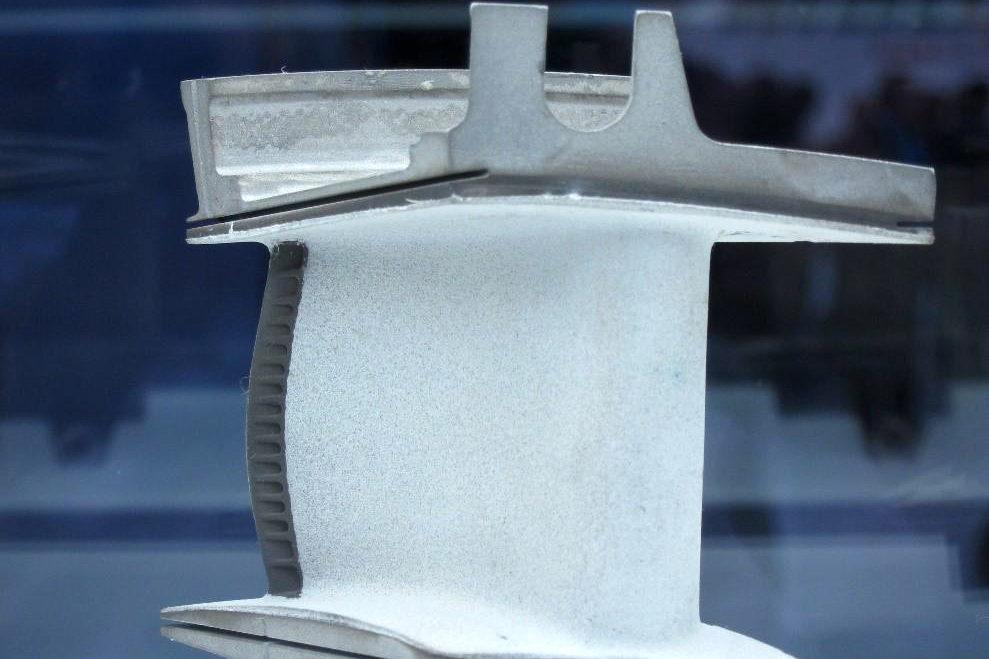
The bond coat is the critical interface between the superalloy substrate and the ceramic top coat, directly influencing adhesion, oxidation resistance, and thermal fatigue durability. It enables TBC systems applied through thermal barrier coating processes to form a stable oxide layer that protects the substrate. In turbine blades produced via single crystal casting, the bond coat ensures long-term adhesion and prevents delamination during extreme thermal cycling.
Types and Performance Impact
Two main bond coat types are used: diffusion coatings (such as aluminides) and overlay coatings (like MCrAlY). Diffusion coatings offer good oxidation resistance but limited strain tolerance. MCrAlY coatings—commonly applied via plasma spraying—provide superior fatigue resistance and are preferred for rotating turbine components fabricated using superalloy directional casting and powder metallurgy methods.
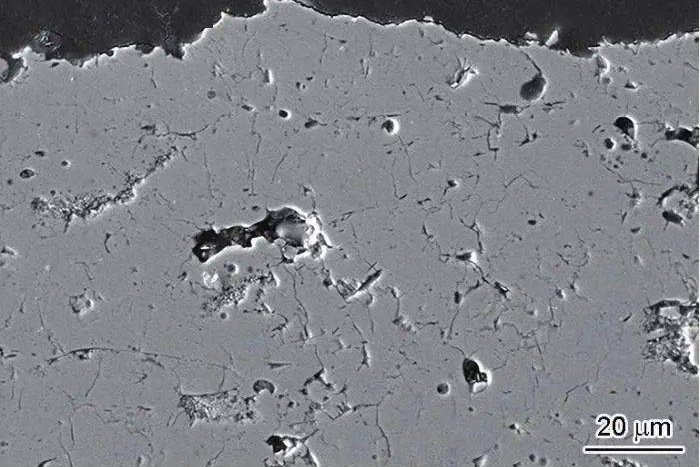
Oxidation Barrier and Thermally Grown Oxide
The bond coat supports the formation of a thermally grown oxide (TGO) layer during service. A stable, slow-growing oxide layer protects the substrate and helps maintain coating integrity. If the bond coat composition is not optimized for the base alloy—such as Inconel 939 or Rene 77—the TGO may grow unevenly, causing stress accumulation and increasing the chance of spallation.
Strain Tolerance and Thermal Fatigue Prevention
A high-quality bond coat improves strain tolerance by accommodating thermal expansion mismatch between the ceramic layer and metallic substrate. In engines operating under rapid thermal cycles—common in aerospace and aviation—this property is essential for preventing crack initiation and delamination. For high-stress components such as turbine discs made with powder metallurgy turbine disc technology, bond coat selection significantly affects operational lifespan and safety margins.
Inspection and Maintenance
Post-application inspection through material testing and analysis ensures adequate bond coat thickness, adhesion strength, and oxide layer formation. If degradation or bond coat fatigue is detected, recoating or localized repair is performed before final finishing via superalloy CNC machining to restore dimensional accuracy.