What tests verify the quality and durability of TBCs on high-temp alloy parts?
Purpose of TBC Testing
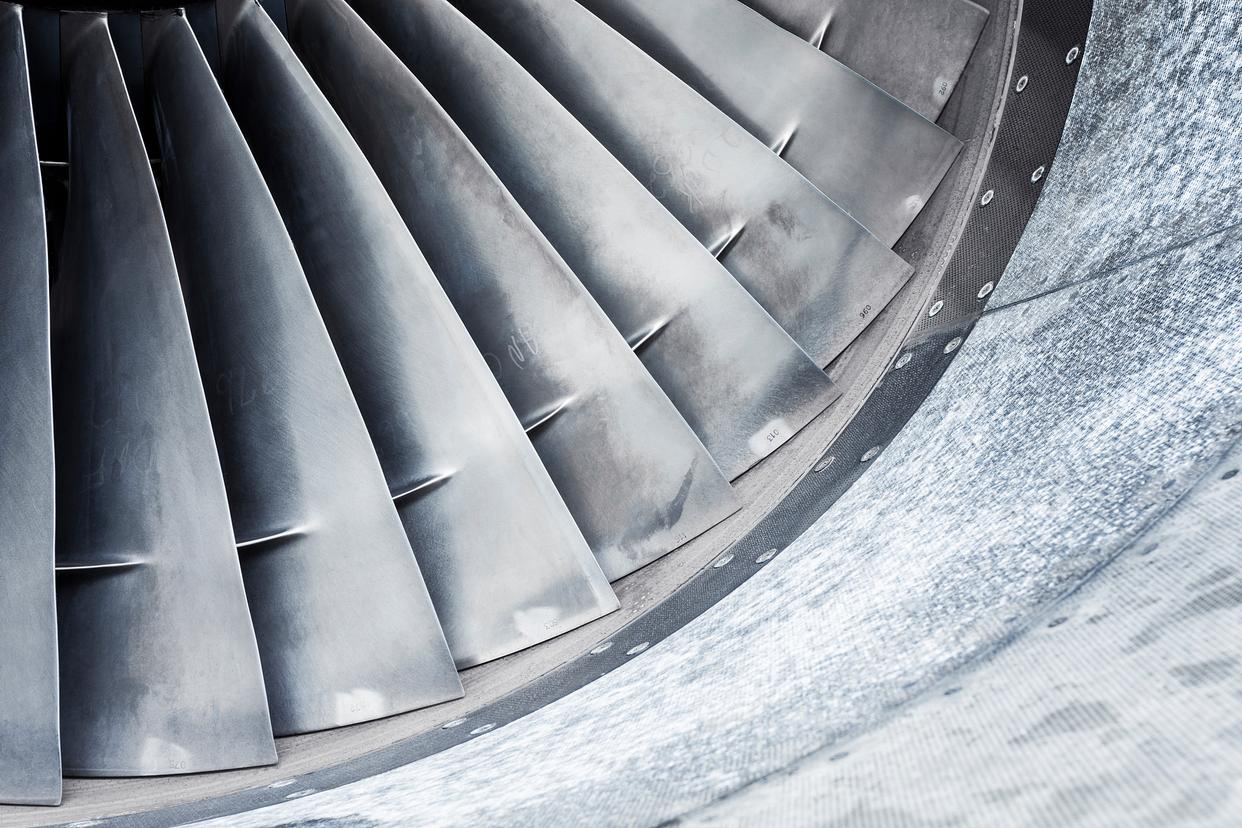
Quality testing of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) ensures that coated high-temperature alloy components can withstand extreme heat, thermal cycling, vibration, and corrosive environments. These evaluations are critical for turbine blades, combustor liners, and hot-section components used in aerospace and power generation systems. Testing is typically conducted after coating application and may follow precision machining processes such as superalloy CNC machining to verify dimensional accuracy prior to service.
Standard Quality Tests
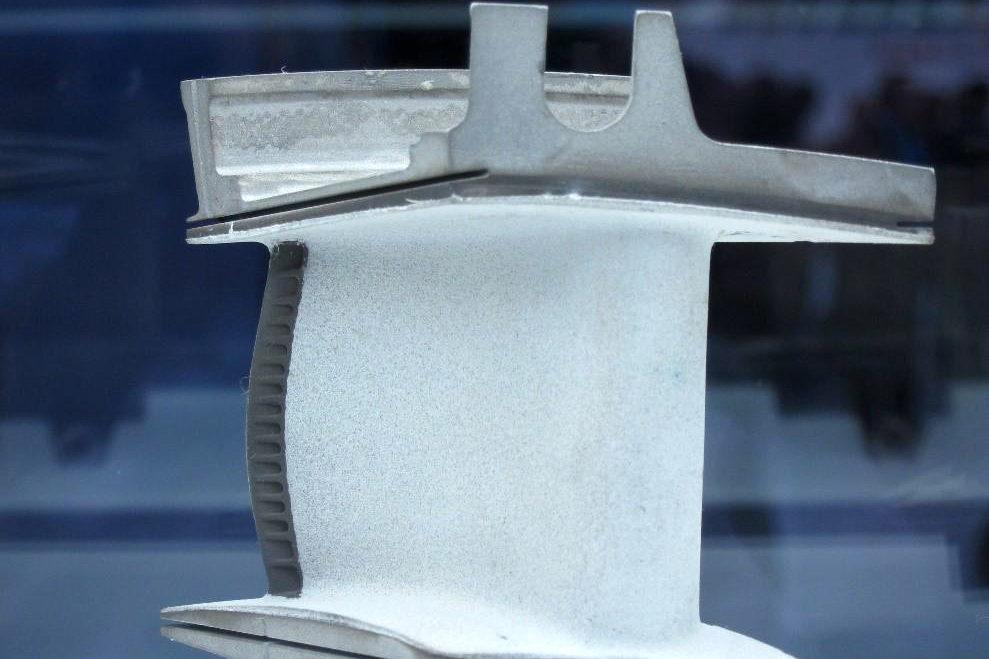
Adhesion Testing (e.g., pull-off or scratch tests) confirms the bond strength between the substrate and TBC layer. Weak adhesion may lead to spallation under thermal stress.
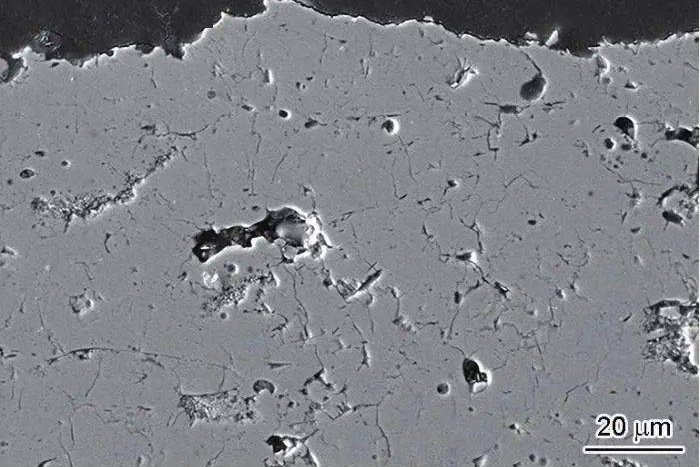
Metallographic Analysis evaluates coating thickness, porosity distribution, and microstructural integrity under cross-sectional observation. This is often combined with material testing and analysis techniques such as SEM and EDS mapping.
Thermal Cycling/Fatigue Testing subjects the coated part to rapid heating and cooling cycles to simulate real engine conditions and detect microcrack formation or delamination.
Advanced Performance Evaluation
Oxidation Resistance Testing verifies the stability of bond coats and alumina formation under high-temperature exposure. Components made via superalloy directional casting require strict oxidation testing to validate structural integrity.
Thermal Shock & Spallation Testing determines how the coating behaves under sudden temperature gradients—critical for turbine blades and combustors operating under fluctuating load conditions.
Creep and Stress-Rupture Testing evaluates how well the TBC-protected substrate resists long-term deformation, especially in single-crystal or directionally solidified components.
Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE)
Techniques such as X-ray, ultrasonic testing, and CT scanning are used to detect internal delamination, microcracks, or voids without damaging the component. These are essential for high-value aerospace parts, often followed by repair or coating refurbishment using TBC treatment services.
Summary
Adhesion tests, metallography, thermal fatigue testing, oxidation resistance evaluation, and non-destructive inspection are key methods for verifying TBC quality and durability. Combined with precision post-processing, they ensure reliable performance of high-temp alloy parts in extreme operating environments.