Why is post-processing necessary for exhaust system components?
Introduction
Post-processing is a crucial stage in the manufacture of exhaust system components. It ensures that the parts produced through casting, forging, or additive manufacturing achieve the mechanical, thermal, and surface characteristics required for reliable long-term operation. Components in automotive, aerospace, and energy systems are subjected to continuous exposure to high temperatures, corrosive gases, and mechanical vibrations—conditions that require exceptional material integrity and surface quality.
Improving Density and Structural Integrity
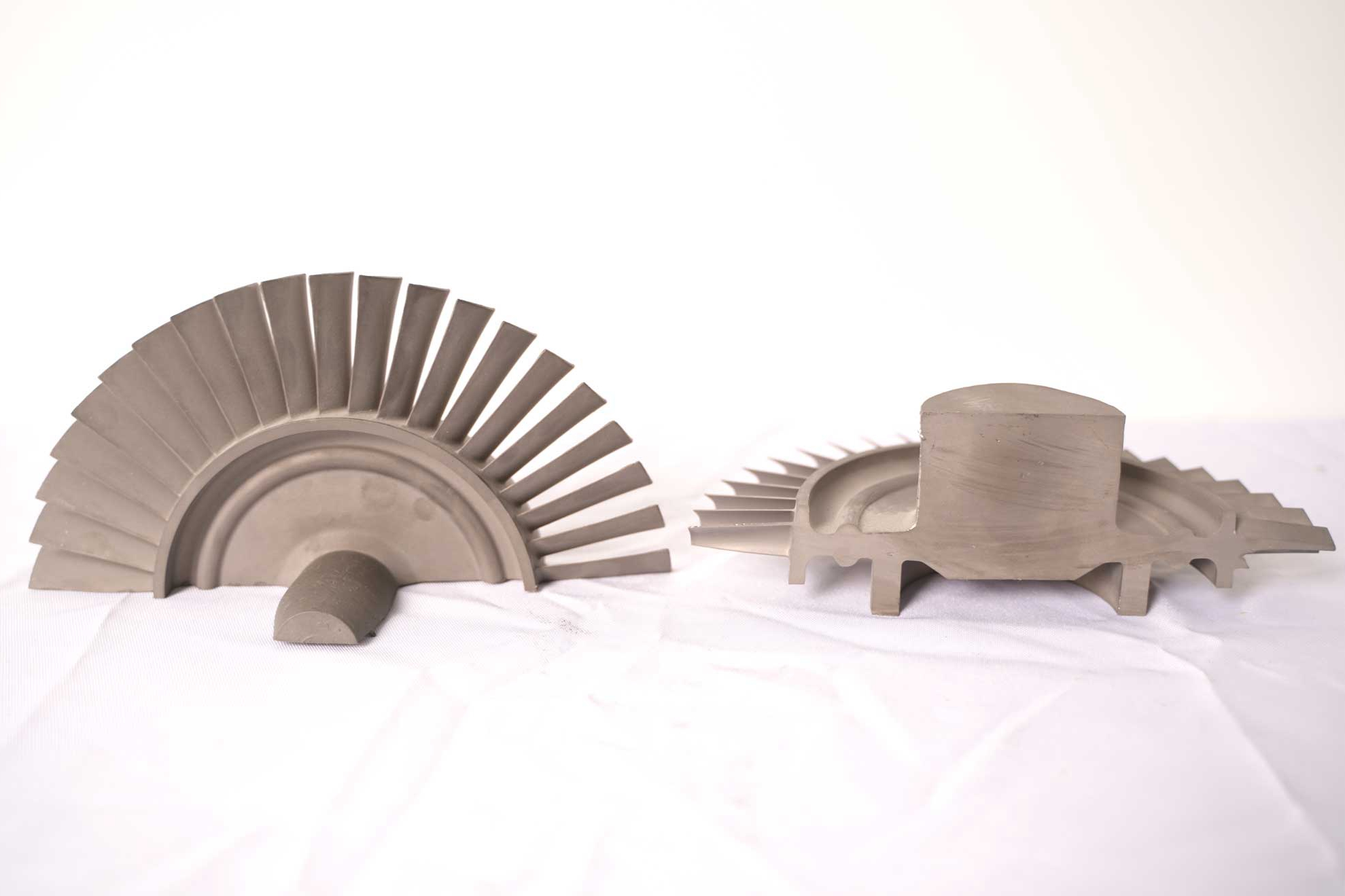
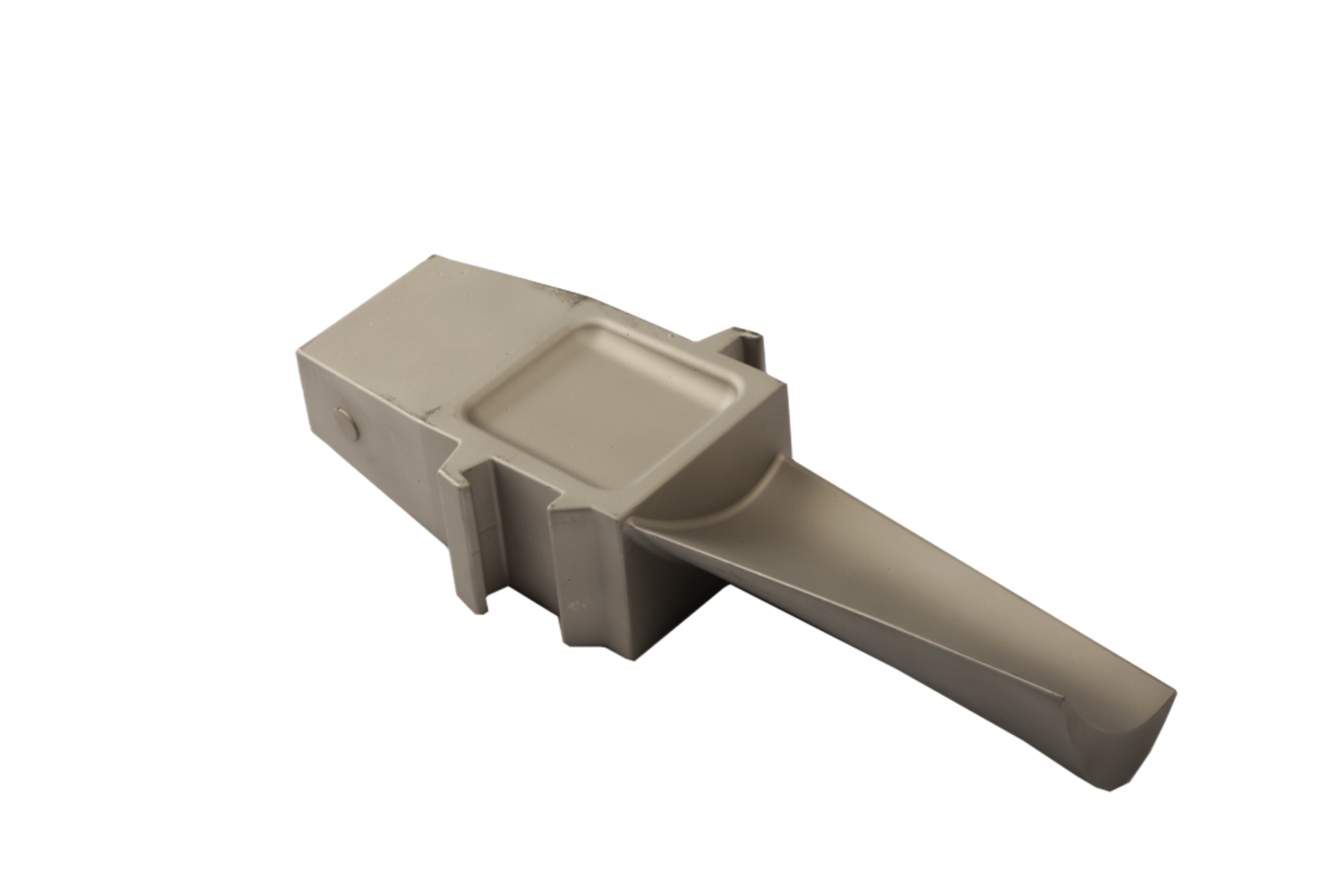
Processes such as hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are fundamental for removing internal voids and porosity in components made from Inconel 718, Hastelloy X, or Rene 80. These high-temperature superalloys are typically used in exhaust manifolds and turbine housings where structural integrity is critical. By applying uniform pressure and temperature, HIP consolidates microvoids, improving fatigue resistance and creep strength under high-stress environments.
Enhancing Mechanical and Thermal Properties
Superalloy heat treatment adjusts the microstructure of nickel-, cobalt-, or titanium-based alloys to optimize strength, hardness, and oxidation resistance. This process aligns grain boundaries, enhances carbide distribution, and stabilizes the material against high-temperature fatigue. When combined with superalloy precision forging, heat treatment ensures components maintain uniform mechanical performance throughout their service life.
For titanium parts such as Ti-6Al-4V, heat treatment and stress-relief processes are essential to prevent distortion and improve toughness, especially after superalloy 3D printing.
Surface Finishing and Corrosion Resistance
Surface quality has a direct impact on exhaust efficiency and durability. Techniques such as superalloy CNC machining and superalloy welding provide smooth mating surfaces and precise joints, thereby reducing gas leakage and vibration fatigue. Furthermore, thermal barrier coating (TBC) protects components from oxidation and thermal degradation, especially in areas near turbine outlets or catalytic converters.
These surface treatments extend component lifespan and ensure consistent thermal performance, even under extreme heat exposure cycles.
Ensuring Compliance and Quality Control
Post-processing also involves material testing and analysis to verify microstructure, hardness, tensile strength, and chemical composition. This step is crucial for industries such as aerospace and aviation, automotive, and power generation, where exhaust systems must meet rigorous safety and performance standards.
Non-destructive testing (NDT), metallography, and dimensional inspections help identify subsurface defects or deviations from design specifications, ensuring every part meets operational reliability requirements.
Conclusion
Post-processing transforms raw or semi-finished exhaust components into high-performance, reliable products that can endure severe thermal and mechanical stress. By combining HIP, heat treatment, coating, machining, and testing, manufacturers ensure enhanced durability, performance stability, and compliance across demanding industrial applications.