How does the post-processing of superalloy parts enhance their performance?
Defect Elimination and Structural Stability
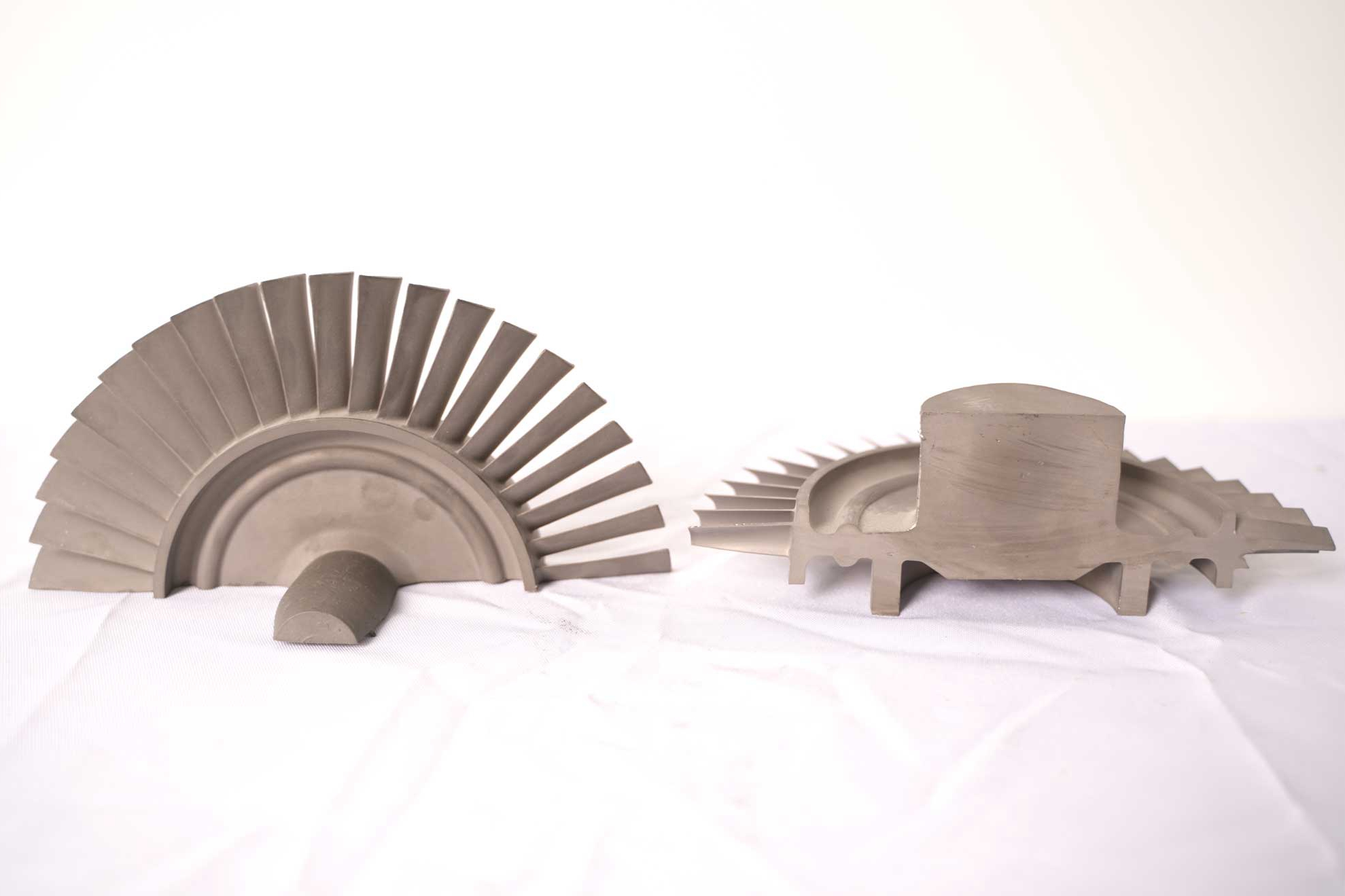
During casting or 3D printing, internal porosity and microcracks are inevitable in superalloys. These defects significantly reduce fatigue life and creep resistance. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is one of the most critical post-processing techniques, as it applies high temperatures and high pressures to close internal voids and improve structural uniformity. As a result, mechanical strength, durability, and thermal fatigue resistance are substantially enhanced, especially in rotating or high-load components.
Microstructure Optimization
Heat treatment plays a vital role in stabilizing the grain structure of alloys such as Inconel 718 and advanced alloys like Rene 65. Controlled heating and cooling cycles enable the achievement of the desired phase distribution and minimize residual stress. Through dedicated superalloy heat treatment, engineers can fine-tune precipitation hardening, grain orientation, and creep resistance to meet specific operating temperatures.
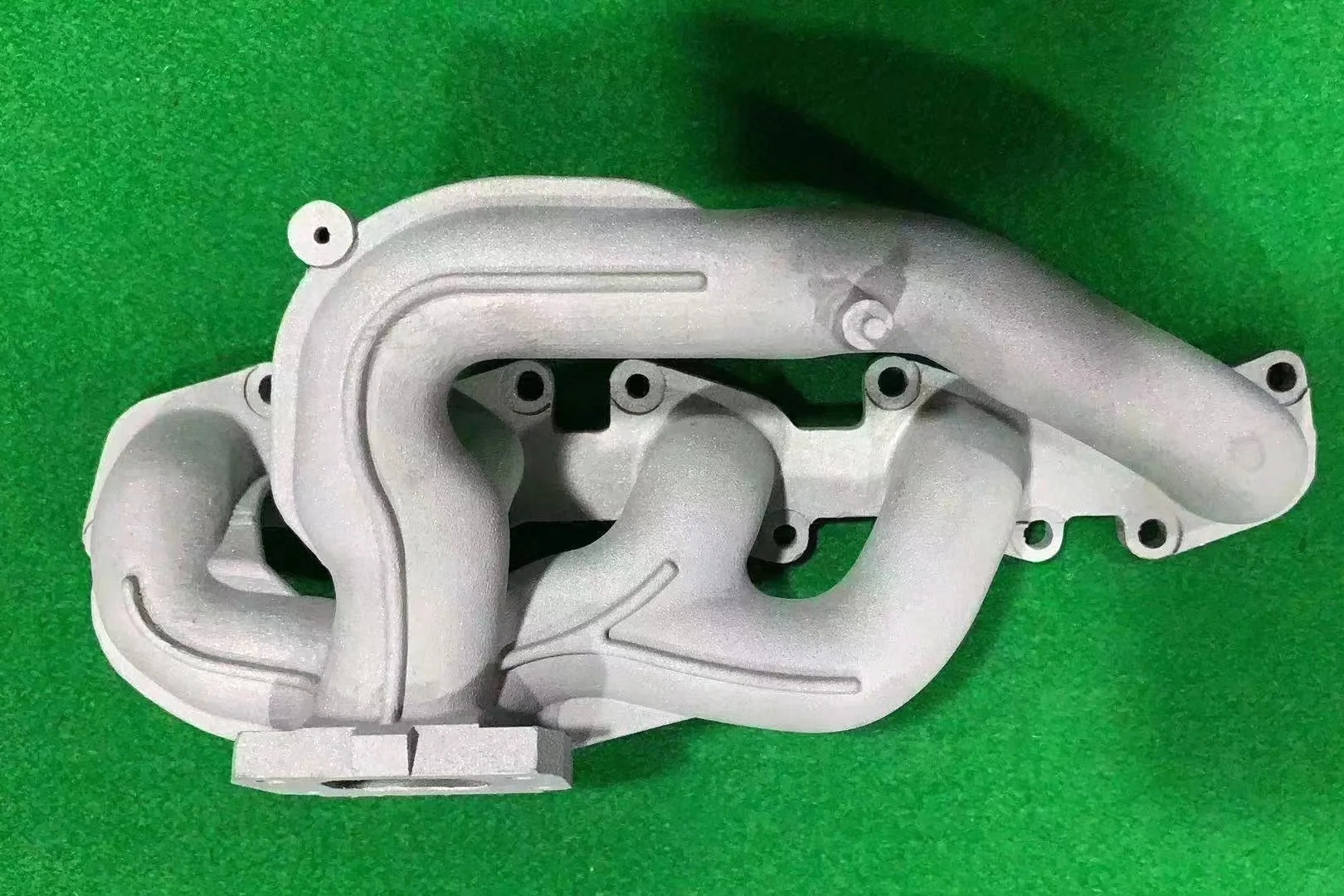
Precision Machining for Functional Fit
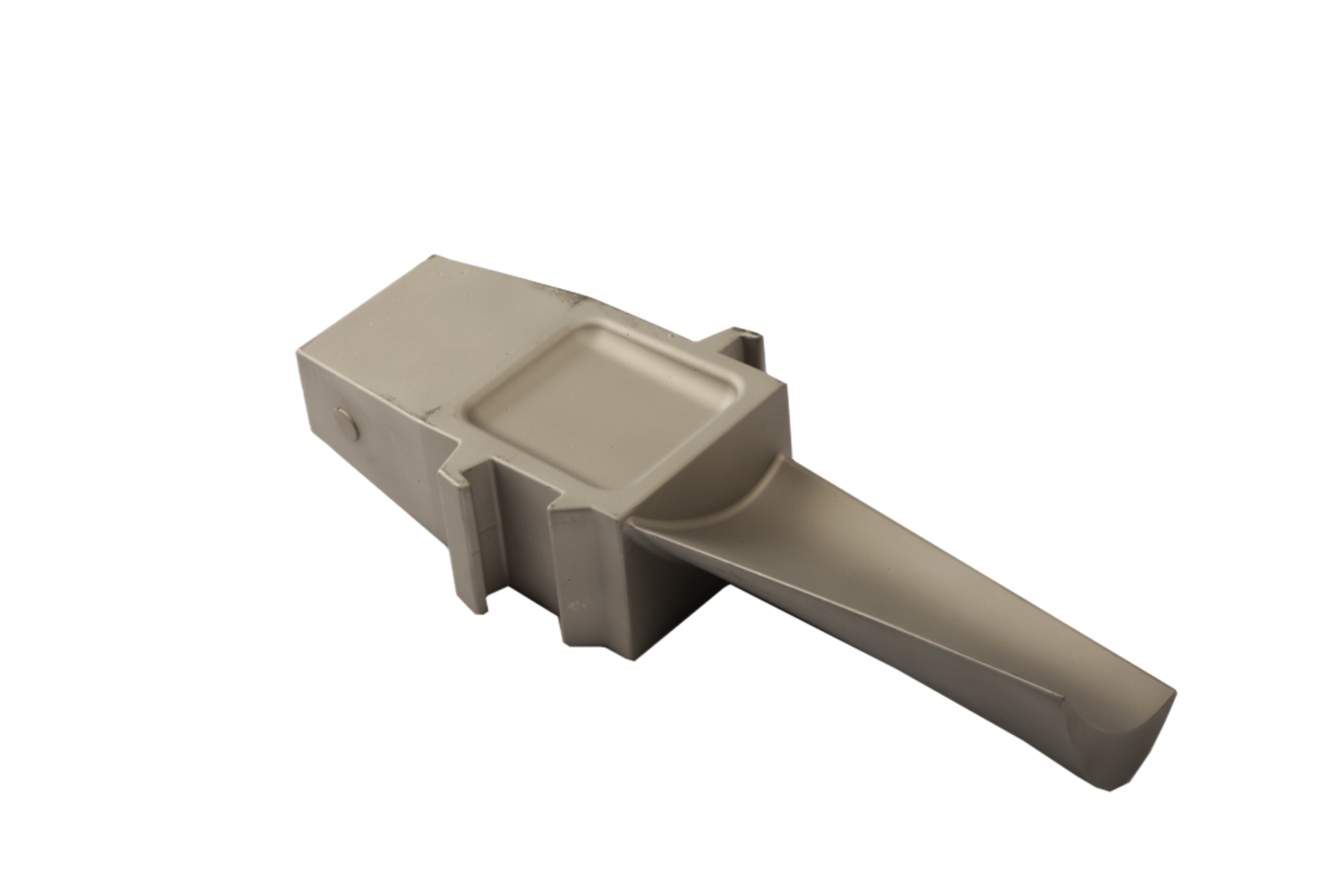
Most superalloy components require tight tolerances and high surface quality for assembly. Processes such as superalloy CNC machining, deep hole drilling, and electrical discharge machining (EDM) enable accurate shaping, ensuring that sealing interfaces, cooling channels, and turbine contours meet design requirements. Machining is often paired with stress-relief thermal treatment to avoid distortion during service.
Surface Enhancement and Environmental Protection
To resist oxidation, corrosion, and high-velocity particle erosion, coatings are frequently applied. Systems such as thermal barrier coating (TBC) provide insulation and protect metal substrates from extreme exhaust or combustion temperatures. After coating, final quality checks and material testing and analysis ensure coating adhesion and long-term performance.
Validation for Critical Industries
Industries such as aerospace and aviation and power generation demand stringent certification. Post-processing ensures compliance with fatigue life, oxidation resistance, and dimensional accuracy. The combination of HIP, machining, heat treatment, and coating yields components that can withstand prolonged service under extreme stress and temperature conditions.