What post-processing techniques are used to improve the quality of superalloy valve components?
Introduction
Superalloy valve components are subjected to demanding service conditions in various sectors, including aerospace, power generation, and oil and gas. After initial casting or forging, post-processing is essential to enhance structural integrity, dimensional accuracy, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Each stage is precisely engineered to refine the material’s microstructure and ensure compliance with performance standards.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for Defect Elimination
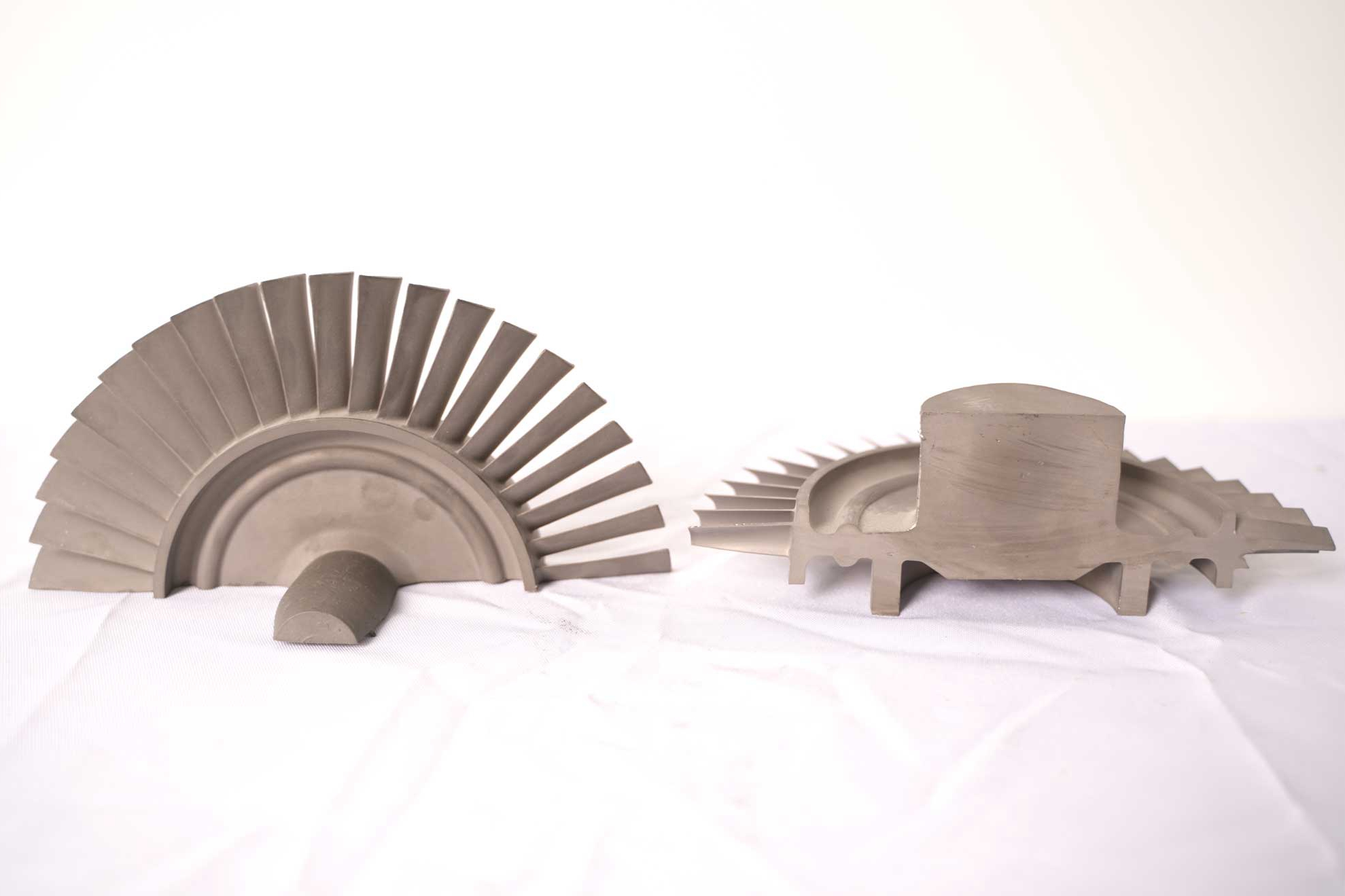
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a fundamental process that removes internal porosity within cast or additively manufactured components. By applying high pressure and temperature simultaneously, HIP densifies the alloy, improving fatigue life and creep resistance. It is particularly important for valve bodies and discs produced through Vacuum Investment Casting or Superalloy 3D Printing. This step ensures structural homogeneity before subsequent machining.
Heat Treatment for Microstructural Optimization
Superalloy Heat Treatment refines the grain structure, stabilizes the γ′ phase, and enhances mechanical properties. Aging and solution heat treatment cycles tailor hardness, ductility, and stress resistance. For alloys such as Inconel 718 or Rene 77, precise temperature control ensures uniform phase precipitation, critical for valves operating under cyclic thermal loads.
Surface Coatings for Oxidation and Erosion Protection
Superalloy Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) provides high-temperature oxidation resistance, extending component life in turbines and combustion environments. Coatings such as ceramic or MCrAlY are applied to valve seats and stems to minimize wear and corrosion. These coatings serve as thermal shields, protecting superalloy substrates from rapid degradation during service.
Precision Machining and Finishing
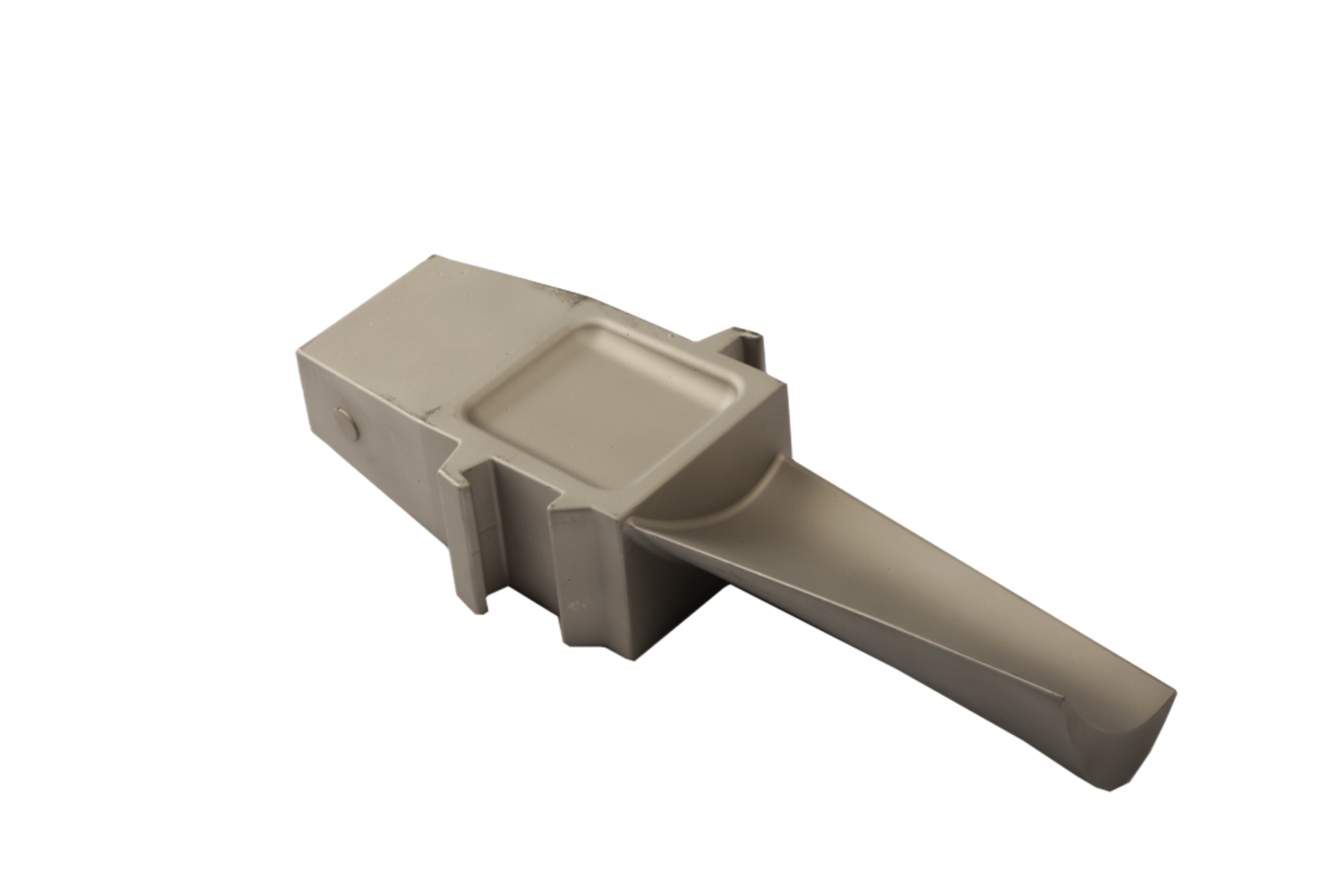
After heat treatment, precision finishing processes like Superalloy CNC Machining and Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) achieve tight tolerances and smooth sealing surfaces. Superalloy Deep Hole Drilling enables the formation of internal channels for complex valve geometries. These processes guarantee leak-free operation and excellent dimensional control, even in high-pressure environments.
Welding and Repair Processing
Superalloy Welding is often employed for joining valve seats, overlaying hard surfaces, or repairing casting defects. Controlled heat input and filler compatibility are crucial to prevent cracking or microstructural degradation. Post-weld heat treatment further restores mechanical consistency across the joint, maintaining uniform hardness and toughness.
Testing and Quality Validation
Material Testing and Analysis verifies the success of post-processing stages. Non-destructive testing (NDT), microstructural analysis, and mechanical evaluation confirm that no defects or thermal anomalies remain. Alloys such as Hastelloy C-22, Stellite 6B, and Nimonic 105 are rigorously tested before approval for service.
Industrial Applications
Post-processed superalloy valves are critical in:
Aerospace and Aviation: turbine fuel and hydraulic control valves.
Power Generation: high-pressure steam and bypass valves.
Oil and Gas: subsea and refinery corrosion-resistant systems.
Conclusion
Post-processing is indispensable for ensuring the performance and reliability of superalloy valve components. From densification and heat treatment to coating and precision machining, each step contributes to a durable and high-performing final assembly capable of operating in the harshest industrial environments.