What post-processing methods are essential for gas turbine components?
The Role of Post-Processing in Turbine Performance
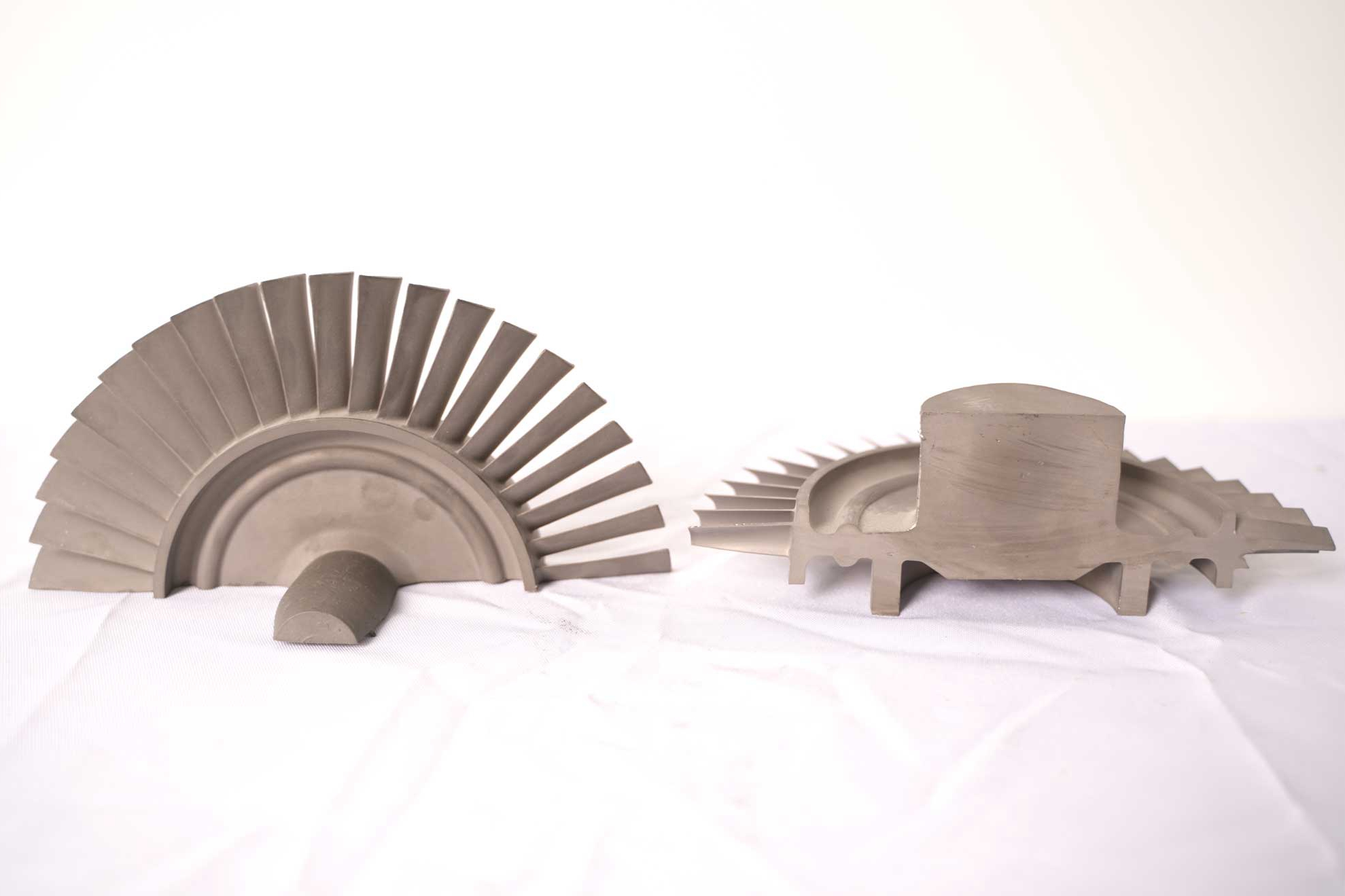
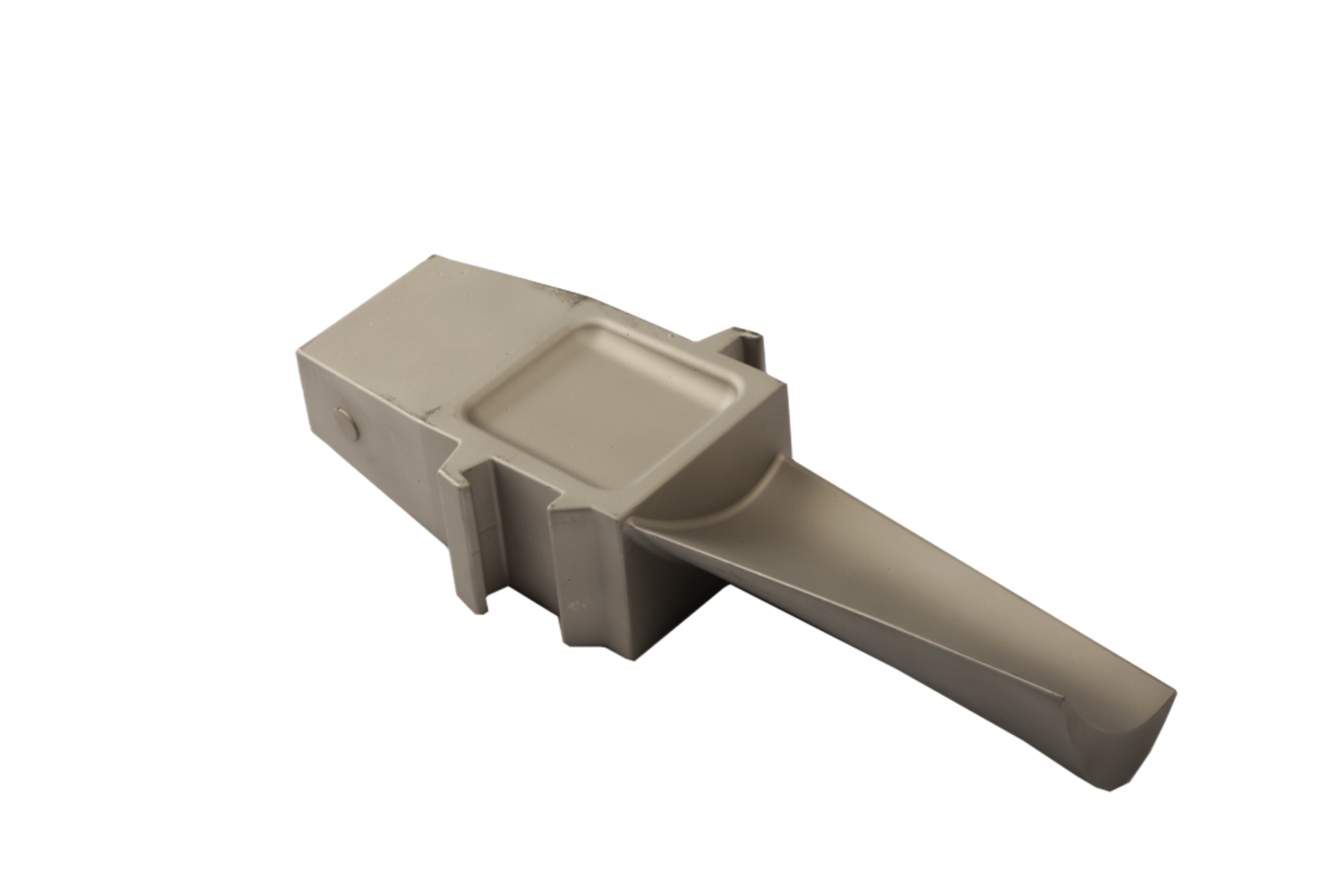
Post-processing is a crucial stage in the manufacturing of gas turbine components, ensuring that each part achieves the mechanical strength, dimensional precision, and surface integrity necessary for operation under extreme thermal and mechanical loads. After casting, forging, or additive manufacturing, turbine components, such as blades, vanes, and discs, undergo a sequence of refining treatments to enhance their durability, creep resistance, and oxidation resistance. The synergy between these processes directly determines turbine efficiency, fuel economy, and lifecycle reliability.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and Heat Treatment
One of the most critical post-processing steps is hot isostatic pressing (HIP). HIP removes internal porosity in components produced through vacuum investment casting or superalloy 3D printing. By applying high pressure and temperature simultaneously, it enhances isotropic strength and fatigue resistance, ensuring long-term stability for components such as turbine blades and combustor rings.
Following HIP, superalloy heat treatment is applied to optimize the microstructure. This process adjusts γ’ precipitate distribution in alloys such as Inconel 718, Rene 80, and CMSX-4, enhancing creep strength and high-temperature stability.
Surface Enhancement and Protective Coatings
Surface treatment plays a vital role in resisting oxidation and thermal degradation. The most common approach is the thermal barrier coating (TBC), which applies ceramic layers to hot-section components, protecting them from exposure to combustion gases above 1100°C.
Complementary to TBC, superalloy welding is used to repair casting defects or restore worn geometries, maintaining component integrity and extending service life. For fine finishing and dimensional accuracy, superalloy CNC machining and electrical discharge machining (EDM) deliver the high tolerances required for aerodynamic profiles.
Testing and Validation
Post-processing concludes with comprehensive material testing and analysis, verifying grain size, phase composition, and mechanical strength. This ensures the component’s compliance with stringent aerospace and power generation standards. Additionally, non-destructive evaluation, such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing, confirms that the applied treatments have eliminated porosity and residual stress.
Industrial Applications
Post-processing is critical across the aerospace, aviation, military, and defense sectors, where even the smallest flaw can lead to catastrophic performance loss. For high-stress turbine sections, integrating HIP, heat treatment, and surface coatings ensures maximum reliability and extended operational life.
Conclusion
Every post-processing step—from HIP and heat treatment to precision machining and coating—collectively transforms raw castings into high-performance turbine components. By refining microstructure, improving surface protection, and ensuring dimensional accuracy, post-processing guarantees that gas turbines perform with optimal efficiency, safety, and longevity.