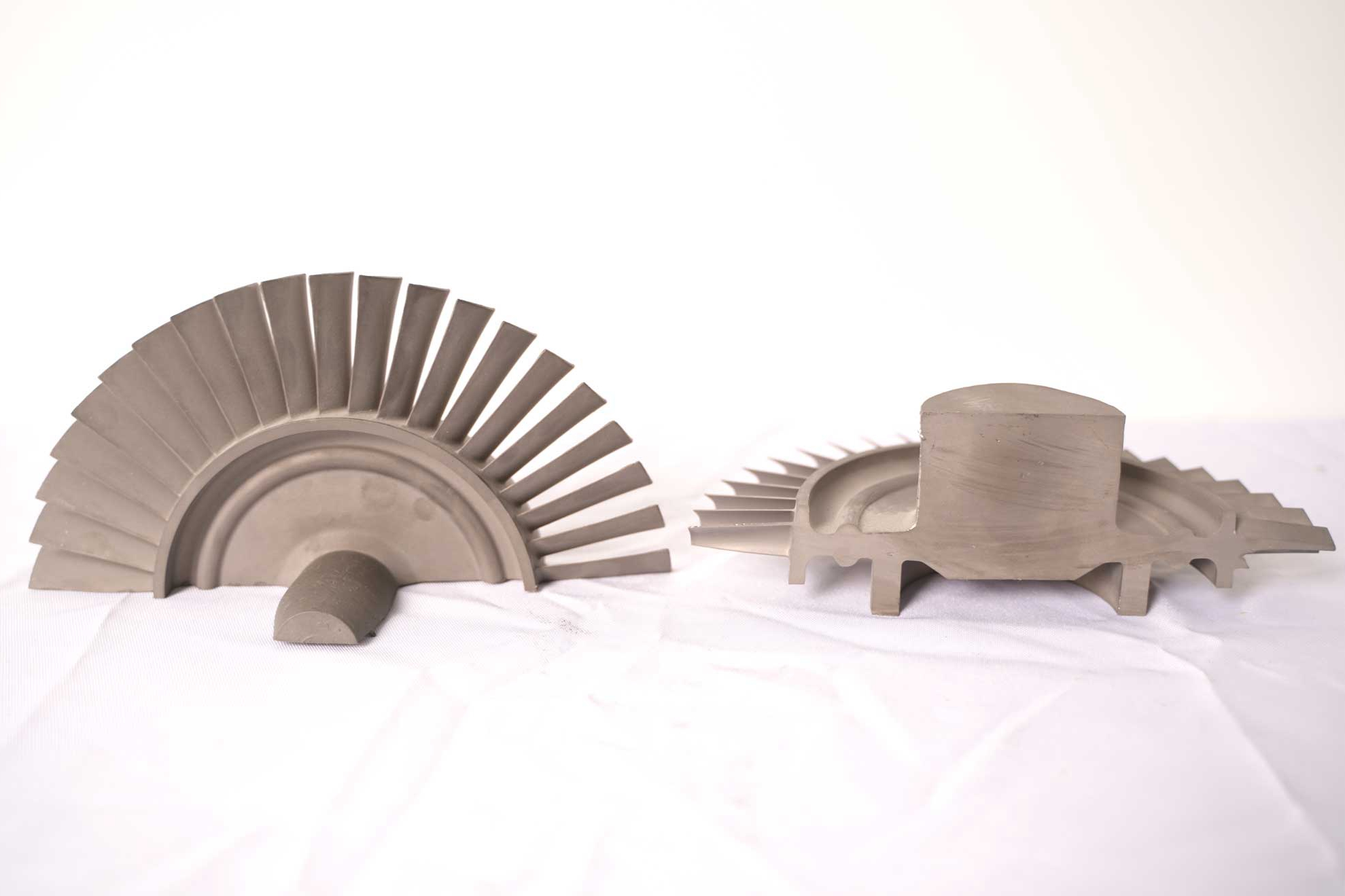
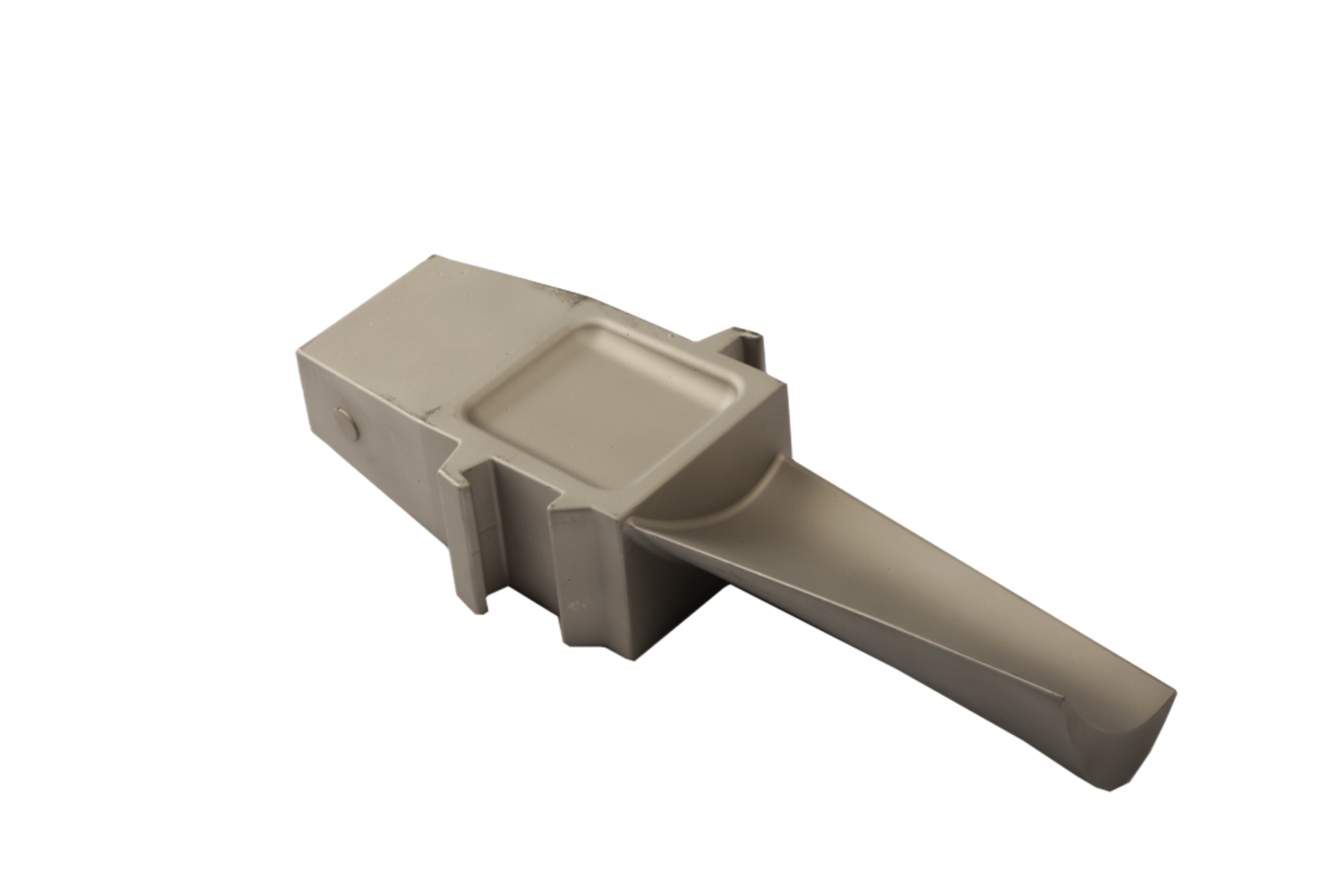
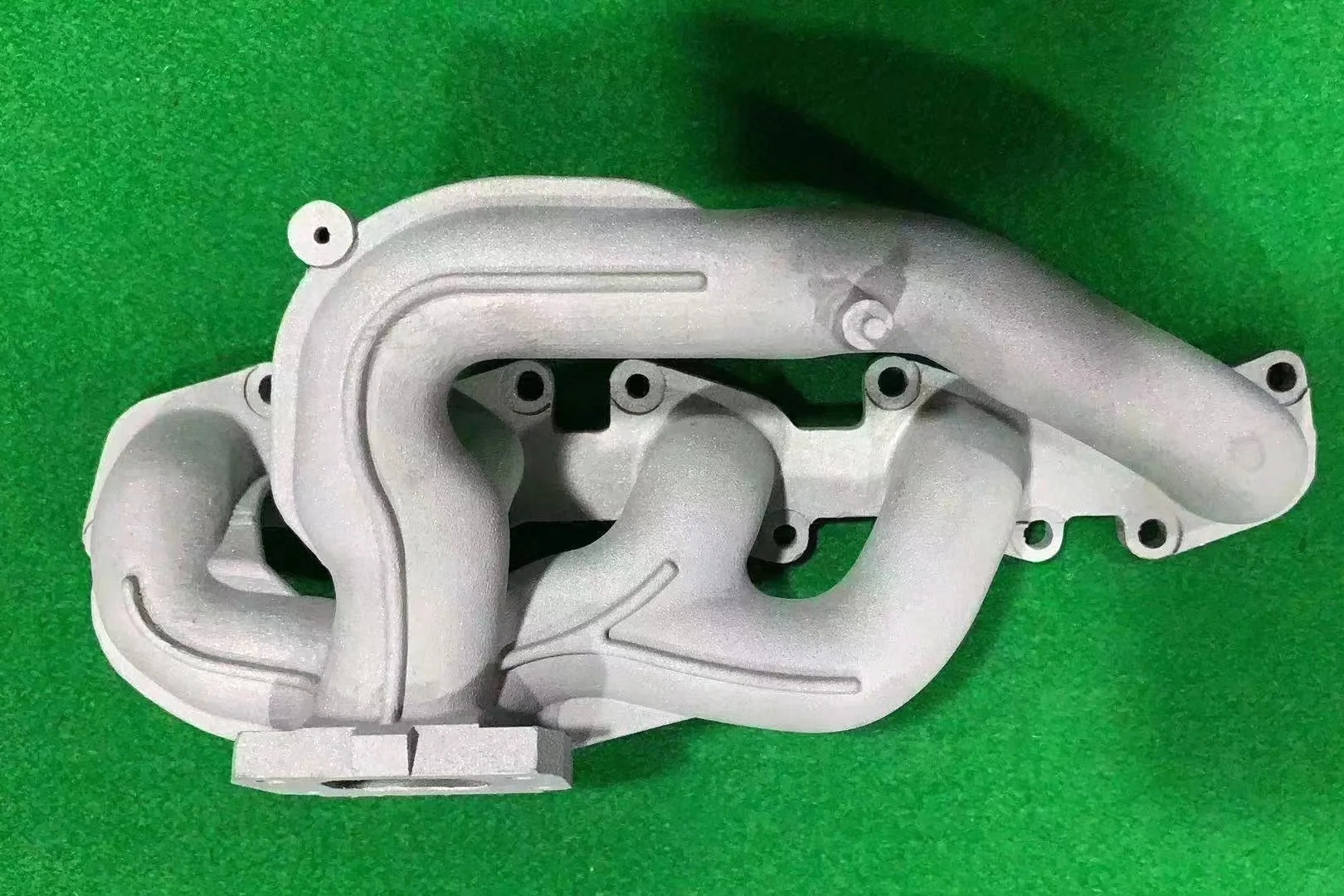
What post-processes are typically applied to superalloy free-forged parts?
Heat Treatment for Microstructure Optimization
After free forging, superalloy components undergo controlled superalloy heat treatment to refine grain orientation, relieve internal stresses, and stabilize phase distribution. Processes such as solution treatment, aging, and stress-relief annealing enhance tensile strength and creep resistance—critical for aerospace and energy components that operate under fluctuating thermal and mechanical loads.
Density Enhancement Through HIP
To eliminate internal voids and improve fatigue life, components often undergo hot isostatic pressing (HIP). This high-pressure thermal process significantly increases part density and resistance to crack propagation. HIP-treated superalloys show superior long-term stability and are better suited for high-cycle environments such as turbine assemblies, nuclear containment systems, and pump units.
Precision Finishing and CNC Machining
Free forging establishes the bulk shape but lacks tolerance accuracy. Final dimensional precision is achieved through superalloy CNC machining, which defines sealing interfaces, functional geometries, and assembly features. Machining prepares parts for coating, welding, and mating with tight-clearance assemblies. Internal channels or complex features can also be produced through deep hole drilling or electrical discharge machining (EDM).
Surface Treatment and Corrosion Protection
To enhance resistance to oxidation, abrasion, and chemical attack, free-forged parts may receive protective coatings such as thermal barrier coating (TBC). Additional surface finishing, polishing, or post-machining inspection ensures compliance with safety-critical requirements and supports long-term functionality across demanding operating environments.
Inspection and Certification
Each post-process step is validated through advanced material testing and analysis, including ultrasonic scanning, X-ray inspection, and dimensional measurements. Documentation and traceability are maintained to meet the standards of aerospace, nuclear, and energy industries before final deployment.